Fig. 2. The effect size of EPA on cognitive function, (a) HRT, (b) HRTISIC and (c) COM, with stratification of baseline EPA levels.
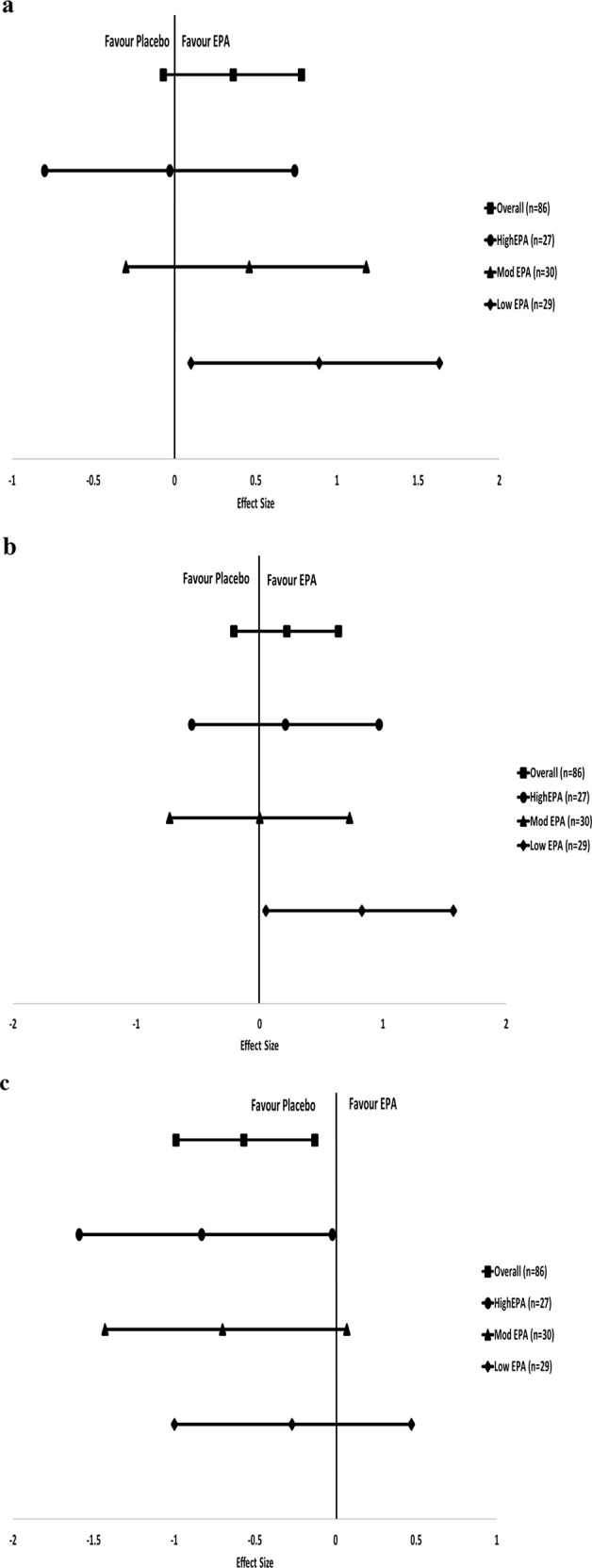
a EPA have a greater effect on HRT than placebo in the Low EPA group, with an effect size of 0.89, the confidence intervals of 0.10 to 1.63, p = 0.015. There were no differences between the n-3 PUFAs group and placebo group on HRT of CPT in the overall, High EPA and Mod EPA group. b EPA have a greater effect on HRTISIC than placebo in the Low EPA group, with an effect size of 0.83, the confidence intervals of 0.05 to 1.57, p = 0.036. There were no differences between the n-3 PUFAs group and placebo group on HRT of CPT in the overall, High EPA and Mod EPA group. c The placebo group improved more on the commission errors than the placebo group in the overall, with an effect size of −0.43, the confidence intervals of −0.84 to −0.01, p = 0.025, and high EPA group, with an effect size of −0.83, the confidence intervals of −1.59 to −0.02, p = 0.022. There were no differences between the EPA group and placebo group on COM of CPT in the Mod EPA and Low EPA group. The x-axis is the effect size. Note, COM, commission errors; EPA, eicosapentaenoic acid; High EPA, EPA > 1.08%; HRT, hit reaction time; HRTISIC, HRT interstimulus interval change; Mod EPA, 0.91% < EPA < 1.08%; Low EPA, EPA < 0.91%; n number
