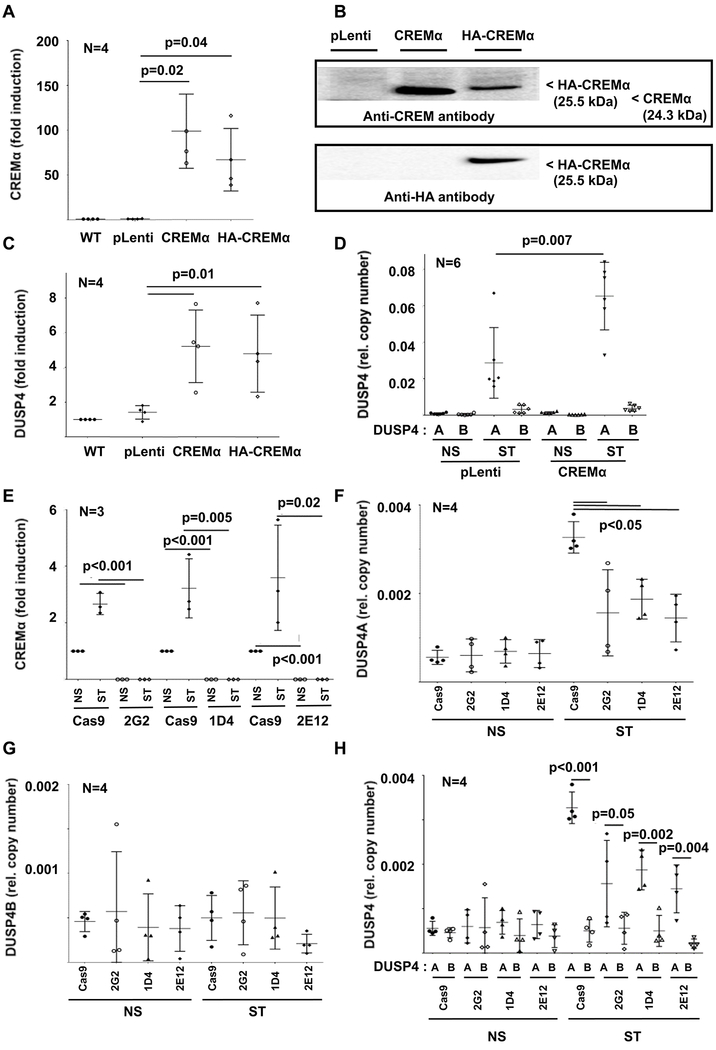
Figure 2: Effects of CREMα expression on DUSP4.
Using lentiviral transduction, CREMα overexpressing cell lines (wild-type CREMα or HA tagged CREMα) and control cell lines (pLenti: transduced with empty plasmid; pLenti_GFP: GPF expression plasmid) were generated. CREMα mRNA (qRT-PCR) (A) and protein (B) expression is increased in both CREMα overexpressing cell lines as compared to controls. Western blots show variable signals or band size depending on molecular weight (in kDa) or targeted epitope (CREM vs HA). Total DUSP4 (qRT-PCR) (C), mainly reflecting DUSP4A (quantitative mRNA probe-based assays) (D) expression is increased in CREMα overexpressing cells (NS: not stimulated; ST: stimulated with plate-bound anti-CD3 and anti-CD28 antibodies). E) In response to stimulation (NS: not stimulated; ST: stimulated) with plate-bound anti-CD3 and anti-CD28 antibodies, CREMα is expressed in increased levels in Cas9 control Jurkat T cells (qRT-PCR). CREM-deficient clones (2G2, 1D4 and 2E12), however, fail to express CREMα under all tested conditions (qRT-PCR). F) Expression of DUSP4A is reduced in CREM-deficient cell lines, while the low expression of DUSP4B (G) is comparable between all cell lines. H) As in primary human CD4+ T cells, DUSP4A expression (black symbols) was significantly higher when compared to DUSP4B (open symbols) (quantitative mRNA probe-based assays). In figures A and C-H means and standard deviations are displayed.