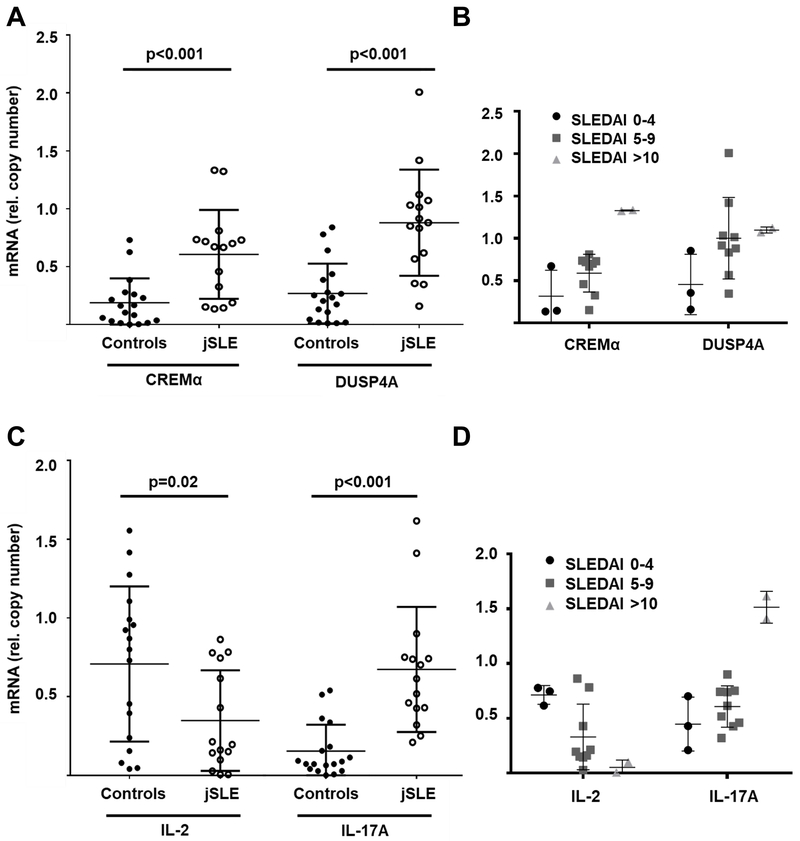
Figure 6: CD4+ T cells from jSLE patients exhibit altered gene expression.
Ex vivo isolated CD4+ T cells from post pubertal patients with jSLE (N=14) exhibit increased expression of CREM isoforms (A), DUSP4A (A), and IL-17A (C) when compared to cells from matched healthy controls (N=17). At the same time, CD4+ T cells from jSLE patients fail to express IL-2 (C), reflecting effector T cell phenotypes previously reported in adult SLE cohorts (quantitative mRNA probe-based assays). Grouping of patient samples based on SLEDAI scores (B,D) (“low”: 0–4; “medium”: 5–9; “high”: >10) suggests associations of higher disease activity with increased CREMα and DUSP4 expression, reduced IL-2 and increased IL-17A expression.