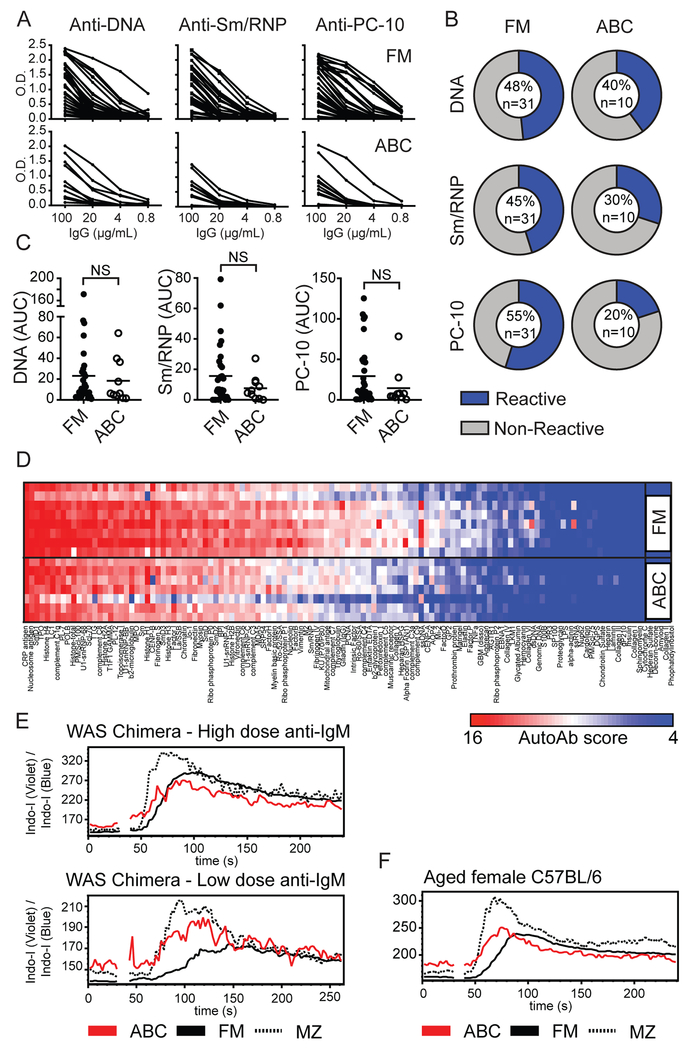
Figure 3: Self-reactivity of ABC repertoire is broadly similar to naïve FM B cells.
(A) ELISA serial dilution curves showing reactivity of mAb cloned from single FM and WAS ABCs towards autoantigens DNA, Sm/RNP, and phosphorylcholine (PC-10). (B) Percentage of mAb reactive to specific autoantigens (blue=reactive clones based on AUC>10, gray=nonreactive clones; numbers within pie chart indicate percentage reactive clones and total number of clones tested). (C) Cloned mAb reactivity by calculated AUC of autoantigen ELISA dilution curves. Each data point indicates an individual mAb. NS=not significant, by Mann-Whitney test. (D) mAb reactivity by autoantigen microarray. Specific autoantigens are ordered from left to right based on intensity of reactivity. Each row represents a pool of 4 randomly selected FM and WAS ABC cloned mAb. (E) Calcium flux following anti-IgM stimulation of CD11b+CD11c+ ABCs (red), FM (solid line), and MZ B cells (dashed line) from representative WAS chimera mouse at 24 weeks post-transplant. Upper panel: High dose anti-IgM (10μg/mL); Lower panel: Low-dose anti-IgM (1μg/mL). (F) Calcium flux in 17-month-old female WT mouse stimulated with 10μg/mL anti-IgM.