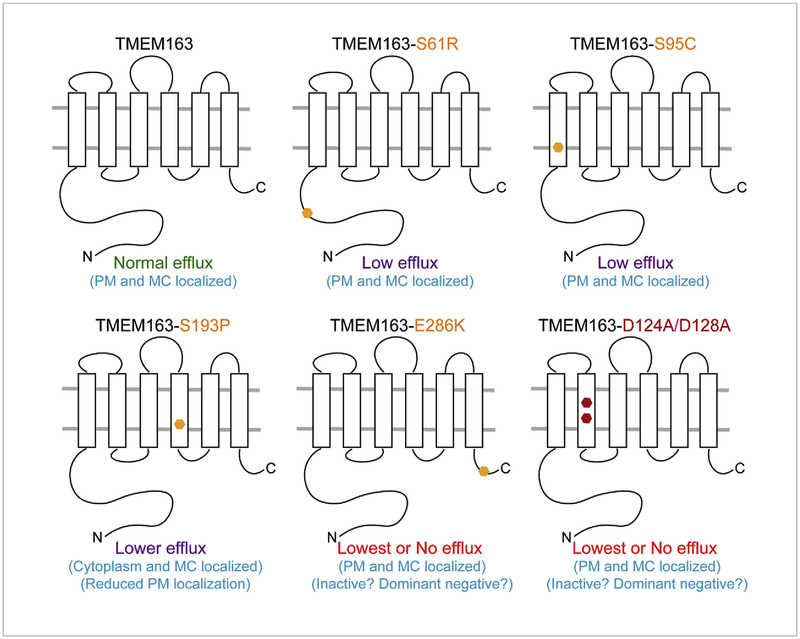
Fig. 5. Schematic diagram summarizing the main observations on the zinc efflux function of TMEM163.
Heterologous expression of the wild-type TMEM163 results in cytoplasmic zinc extrusion in the presence of high zinc levels inside the cells. Expression of the non-synonymous SNPs S61R, S95C, and S193P produces marked reduction of efflux activity when compared with wild-type TMEM163. S61R showed altered protein band migration pattern on WB, suggesting that S61 is a PTM target. S193P is mostly expressed in the cytoplasm and MC as evidenced by CSB and WB, while the other variants are found mostly in the PM and MC. The E286K protein variant has the lowest efflux activity in comparison with other SNPs and wild-type TMEM163. Similar to E283K, the D124A/D128A protein variant has comparably the lowest efflux activity relative to the wild-type TMEM163 and other SNPs. PM, plasma membrane; MC, membrane compartment.