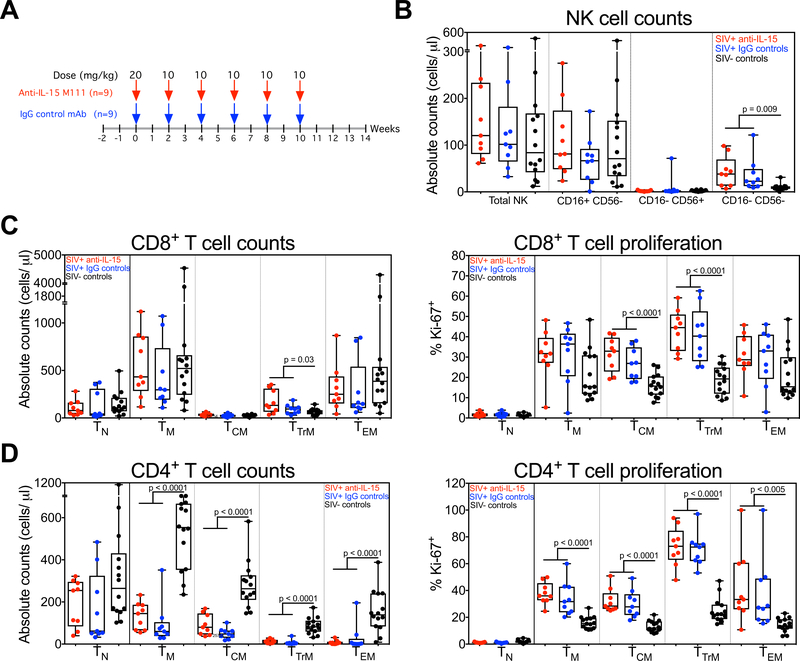
Figure 1. Analysis of T cell and NK cell dynamics in chronic SIV-infected RM prior to IL-15 blockade.
(A) A schematic representation of the study protocol showing SIV-infected RM received 20mg/kg of anti-IL-15 or IgG control mAb on day 0 and 10mg/kg on days 14, 28, 42, 56 and 70. (B) Comparison of absolute NK cell counts, including CD16+ CD56−, CD16− CD56+ and CD16− CD56− subsets in blood of RM on day 0 of anti-IL-15 mAb treatment (n = 9) or IgG control mAb treatment (n = 9) versus SIV-uninfected control RM (n = 14). (C) Comparison of absolute counts and proliferative fraction of CD8+ T cells, including TN, TM, TCM, TTrM and TEM subsets in blood of RM on day 0 of anti-IL-15 mAb (n = 9) or IgG control mAb (n = 9) treatment versus SIV-uninfected control RM (n = 14). (D) Comparison of absolute counts and proliferative fraction of CD4+ T cells, including TN, TM, TCM, TTrM and TEM subsets in blood of RM on day 0 of anti-IL-15 mAb treatment (n = 9) or IgG control mAb treatment (n = 9) versus SIV-uninfected control RM (n = 14). Results are shown as cells/μl of blood for absolute counts or percentage of Ki-67 for proliferation. Each data point represents a single determination from an individual RM. Significance of difference in all parameters was assessed as described in Materials and Methods.