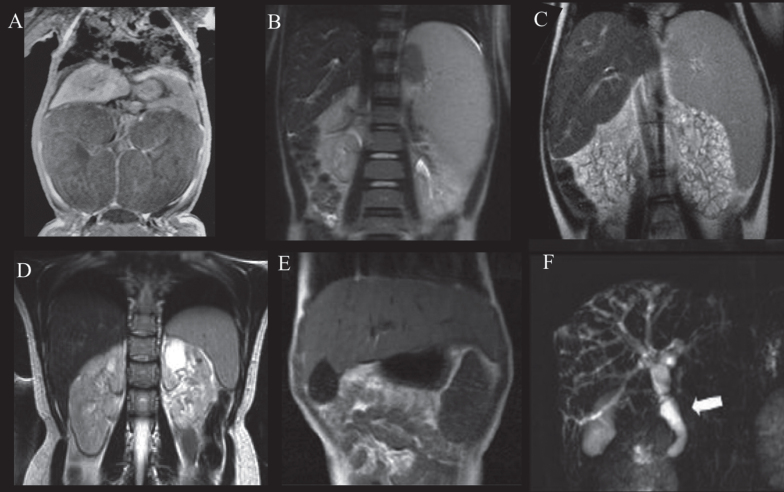
Fig.3.
Abdominal MRI of patients with ARPKD displaying variable severities of liver and kidney disease. A) Newborn with ARPKD with massively enlarged kidneys. B) Seven-year-old boy with markedly enlarged spleen and mild kidney disease with imaging findings limited to parts of the medulla, and normal kidney function. C) Six-year-old girl with markedly enlarged spleen and enlarged cystic end stage kidneys with glomerular filtration rate at 22 mL/min/1.73 m2. D) 24-year-old female with mildly enlarged spleen in association with moderate renal disease affecting the entire medulla but only parts of the cortex and decreased glomerular filtration rate at 55 mL/min/1.73 m2. E) Enlarged left lobe of the liver in congenital hepatic fibrosis extending to the left sub-diaphragmatic area. F) ARPKD patient with Caroli’s syndrome. Fusiform and small cystic dilatations of peripheral and central intrahepatic bile ducts as well as fusiform dilatation of the extrahepatic common bile duct (arrow) and large gallbladder.