Figure 1.
Inturned and Fuzzy Are Longin-Domain Proteins Related to Known Rab GEF Subunits and Form a Rab23 GEF Complex
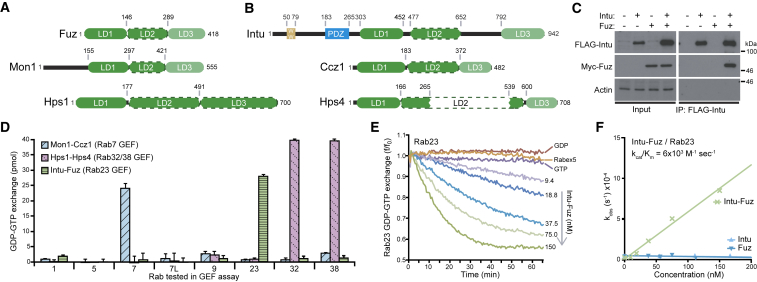
(A and B) Predicted domain structures of H. sapiens (A) Fuz, Mon1, and Hps1 and (B) Intu, Ccz1, and Hps4. Longin (green), PDZ (blue), and WW-like domains (gold) are shown. LD1, LD2, and LD3 indicate the positions of the predicted longin domains, many of which, in particular LD2 of Hps4, are extended beyond the minimal 120 residues by inserts in loops. All LD1s are canonical ββαβββαα longin domains (β, β sheet; α, α helix), all LD2s are αββαββββα circular permuted roadblock longin-type domains (dashed lines), and LD3s are typically ββαβββα lamtor-like longin domains, which lack the final helix (pale green), except for Hps1, where LD3 is of the roadblock type.
(C) HEK293T cells were transfected with FLAG-Intu and Myc-Fuz as indicated. After 24 h, complexes were recovered using FLAG immunoprecipitation and western blotted for Intu and Fuz. Actin was used as a negative control.
(D) GDP-GTP exchange endpoint assays were performed using human Intu-Fuz, Mon1-Ccz1, and Hps1-Hps4 complexes and a subset of Rab GTPases. Mean GDP-GTP exchange in pmol with error bars indicating the SEM for 3 independent experiments are plotted in the graph for each GEF complex.
(E) GDP-GTP exchange activity of Intu-Fuzzy complexes toward Rab23 was measured over time as a function of GEF concentration. Rabex-5 was taken as a negative control. The basal exchange rate in the absence of a GEF was subtracted from the values plotted in the graph.
(F) Initial rates of nucleotide exchange were extracted from these data for the Intu-Fuz complex or the individual subunits and plotted against GEF or subunit concentration for 3 independent experiments. Catalytic efficiency (kcat/KM) toward Rab23 was calculated as described in the STAR Methods.
See also Figure S1.