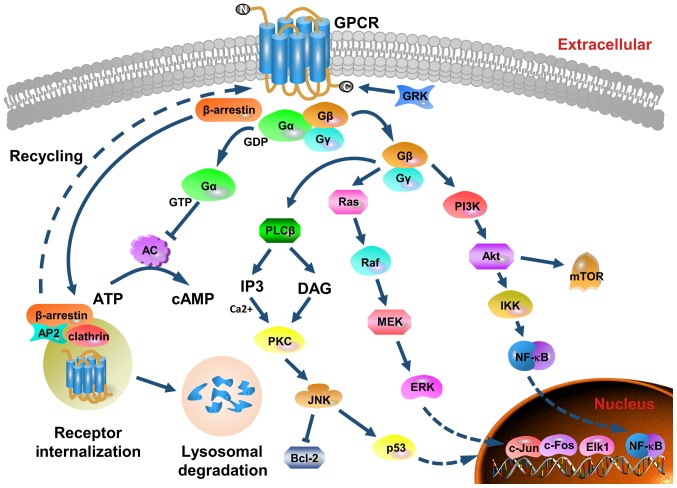
Figure 1.
Structure, major signaling cascades and receptor recycling of CXCR2. CXCR2 belongs to the G protein-coupled receptor family that possesses seven transmembrane structures. It contains an extracellular N-terminus, an intracellular C-terminus, three extracellular loops and three cytoplasmic loops. Following ligand binding, CXCR2 physically couples to the G protein. Subsequently, CXCR2 is activated and the GDP linked to the Gα subunit of the G protein complex is converted to GTP. The Gα subunit coupled to the inner cell membrane dissociates from CXCR2 and the Gβγ subunits. Several downstream pathways are induced, and the main three signaling pathways are via PI3K/Akt, PLC/PKC and Ras/Raf/ERK1/2. Moreover, the Gα subunit inhibits adenylate cyclase activity and decreases the efficiency of ATP conversion to cAMP. GRK phosphorylates the C-terminus of the receptor, and mediates the desensitization and endocytosis of the receptor via β-arrestin recruitment of endocytic components. AP-2 also regulates CXCR2 internalization and sequestration. Internalized CXCR2 is subjected to degradation by lysosomes, or recycled to the outer membrane surface. These pathways modulate cell metabolism, survival, proliferation, apoptosis, angiogenesis, transduction and motility. As a positive feedback loop to enhance CXCR2 functionality is formed by upregulating the expression of cytokines and chemokines. CXCR2, CXC chemokine receptor 2; PI3K, phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase; PLC, phospholipase C; PKC, protein kinase C; ERK, extracellular signal related kinase; cAMP, cyclic AMP; GRK, G-protein coupled receptor kinase; GPCR, G-protein coupled receptor; GDP, guanosine disphosphate; AC, adenylyl cyclase.