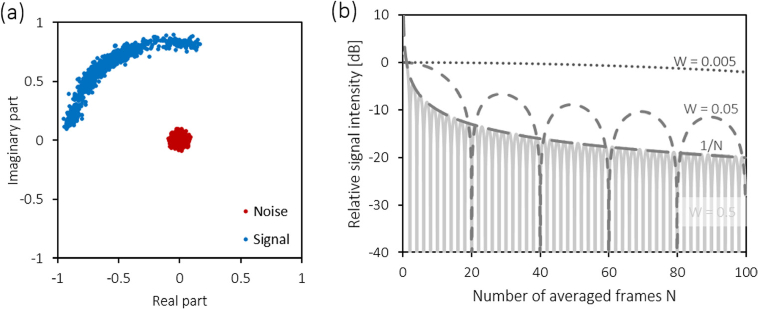
Fig. 9.
Phasor rotation by axial motion and signal penalty after complex averaging of axially displaced signals. (a) Example of a signal phasor trajectory of 1000 repeated measurements of a weak reflector (an attenuated glass surface). Over 1/70 second, the phasor (blue dots) is markedly moving around the origin. Corresponding noise signals are shown as red dots. The main source of displacement in this measurement was air flow from a nearby air condition outlet. (b) Relative signal intensity decrease caused by complex averaging of signals with relative displacements of 0.5 (solid line), 0.05 (dashed line), and 0.005 (dotted line). For reference, is plotted as well. While relative displacements of λ/200 (W = 0.005) between consecutive signals almost do not affect the intensity of the averaged signal, greater displacements such as and cause a periodic, significant signal reduction. In unlucky cases, reaches zero such that the averaged signal is completely annihilated.