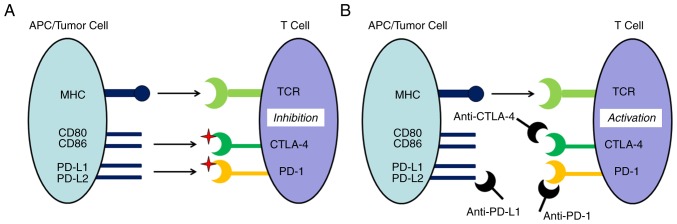
Figure 1.
Principle of immune checkpoints and checkpoint inhibitors. (A) Tumor immune escape, which is the activity of T cells inhibited by the immune checkpoint signaling pathways, including CTLA-4 and PD-1/PD-L1. (B) Immune checkpoint inhibitors, which are monoclonal antibodies against immune system inhibitors, including CTLA-4 and PD-1, and its ligand PD-L1, activate an immune response. MHC, major histocompatibility complex; PD-L, programmed death-ligand; CTLA-4, cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen-4; PD-1, programmed death 1; TCR, T cell receptor; APC, antigen-presenting cell.