Figure 1.
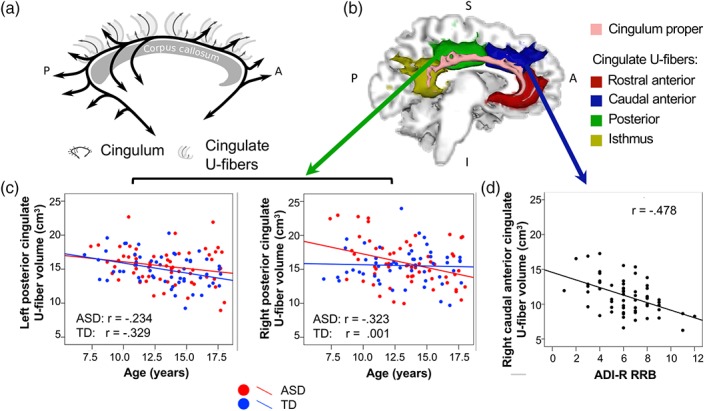
a–d. (a) Schematic representation of the cingulum (in black), defined as fibers that enter the main fiber bundle and travel longitudinally along it before exiting, and cingulate U‐fibers (in gray), defined as short fibers that connect the cingulate cortex with neighboring cortex—these may cross the main bundle portion of the cingulum but do not travel long distances within it. (b) Examples of cingulum proper (pink) and rostral anterior (red), caudal anterior (blue), posterior (green), and isthmus (yellow) cingulate U‐fiber tracts of the left hemisphere (medial view) are shown for an ASD participant (age 17 years). (c) Left posterior cingulate U‐fiber volume decreased with age in ASD and TD (left panel). Right posterior cingulate U‐fiber volume decreased with age in the ASD group only (right panel). (d) Tract volume of the right caudal anterior cingulate U‐fiber was negatively associated with the ADI‐R repetitive subscore in the ASD group.
Abbreviations: ADI‐R, autism diagnostic interview‐revised ; ASD, autism spectrum disorder
