Figure 3.
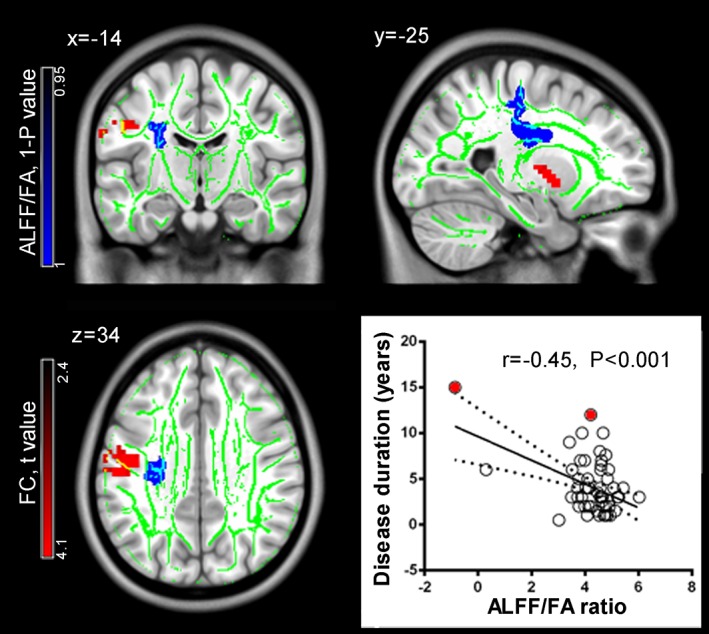
Structural and functional alterations in the left corticobasal ganglia‐thalamocortical network in Parkinson's disease (PD). PD patients exhibit decreased amplitude of low‐frequency fluctuation (ALFF)/fractional anisotropy (FA) ratio in the corticospinal tracts (shown here in blue) and increased white matter (WM)—Gray matter (GM) functional connectivity (shown here in red). The fiber skeleton for tract‐based spatial statistics is illustrated in green. In the patient group, the abnormal ALFF/FA ratio in the corticospinal tract shows a significant negative correlation with disease duration. Notably, this correlation become nonsignificant after removing two statistical outliers marked in red color [Color figure can be viewed at http://wileyonlinelibrary.com]
