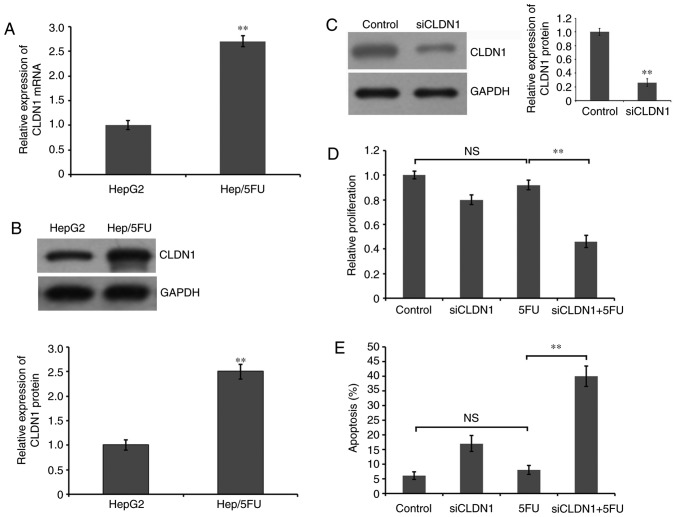
Figure 2.
Role of CLDN1 in proliferation and apoptosis of Hep/5FU cells. (A) Cells were collected and total RNA was extracted for reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction to evaluate the mRNA expression level of CLDN1 in Hep/5FU and HepG2 cells. **P<0.01 vs. HepG2 cells. (B) Cells were collected and lysed, and western blot analysis with an anti-CLDN1 antibody was used to examine the protein level of CLDN1. GAPDH expression level was detected as a reference. The protein bands were quantified by densitometry and the expression levels were expressed as a ratio relative to the expression level in HepG2 cells. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. **P<0.01 vs. HepG2 cells. (C) Hep/5FU cells were transfected with siCLDN1 or negative control for 48 h. Subsequently, western blot analysis was used to detect CLDN1 protein expression using an anti-CLDN1 antibody. GAPDH expression level was detected as a reference. The protein bands were quantified by densitometry and the expression levels were expressed as a ratio relative to the expression level in HepG2 cells. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. **P<0.01 vs. control cells. Hep/5FU cells were transfected with negative control or siCLDN1 and cultured in the presence or absence of 50 mg/l 5-FU for 48 h. (D) Cell proliferation was analyzed with an MTT assay and (E) cell apoptosis was evaluated by Annexin V-fluorescein isothiocyanate/propidium iodide assay. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. **P<0.01. NS, no significance; CLDN1, claudin-1; Hep/5FU, 5-fluorouracil-resistant HepG2; SEM, standard error of the mean; siCLDN1, small interfering RNA targeting claudin-1.