Figure 1.
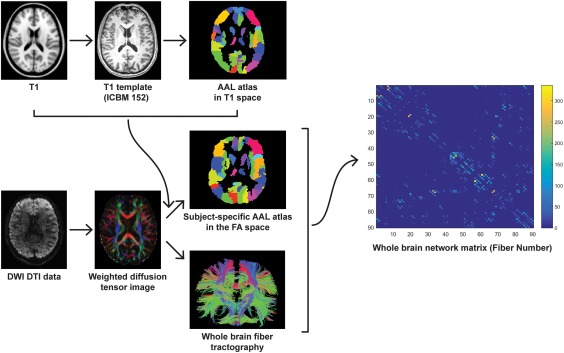
Flowchart for constructing anatomical brain white matter networks. First, nonlinear registration of the structural images to the MNI space and the resulting transformation was inverted and used to warp the AAL atlas (Tzourio‐Mazoyer et al., 2002)—from the MNI space to the T1 space. AAL atlas was employed to parcellation the individual cerebrum into 90 regions, where each region represents a network node (Bullmore & Sporns, 2009). Next, estimation of the diffusion tensors from DWI images was performed. Whole brain white matter fibers were reconstructed using a deterministic tractography method. The AAL atlas in T1 space was then warped to the individual FA space. Finally, the white matter network matrices were constructed using fiber number as a weight and compared between RTS‐VGPs and NVGPs [Color figure can be viewed at http://wileyonlinelibrary.com]
