Figure 4.
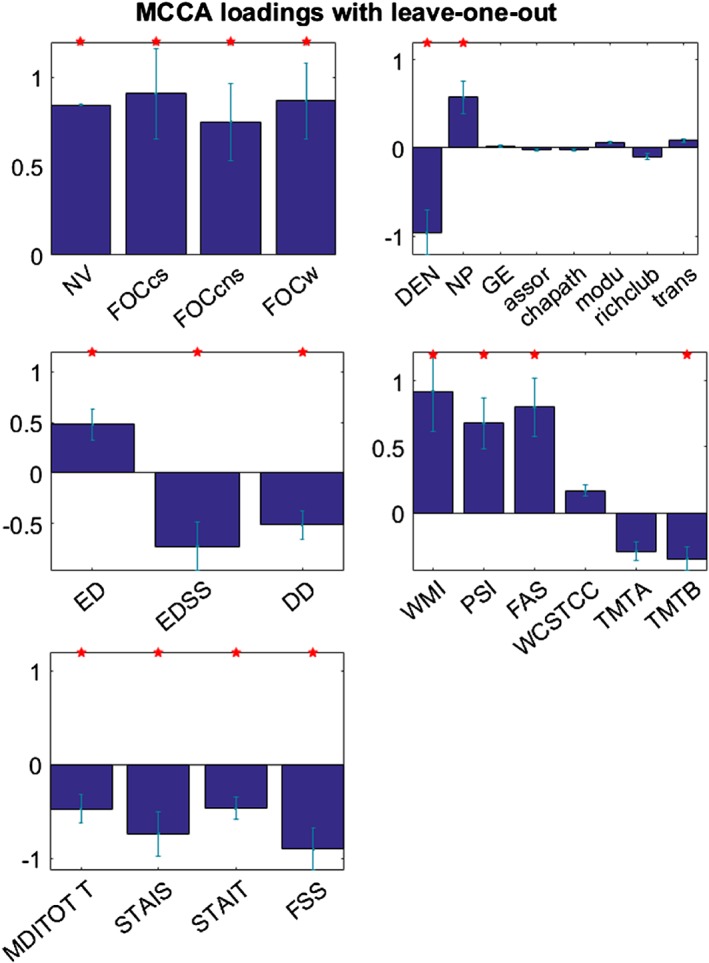
MCCA loadings of all variables in all sets are shown with error bars indicating SEs. Red stars highlight the individual variables that demonstrate significant loadings (p < .05). All the variables that show positive loadings are positively associated with each other. All the variables that present negative loadings are positively correlated with each other. (NV: Network variation, FOCcs: Flexibility of interhemispheric connections, FOCcns: Flexibility of cross‐hemispheric connections, FOCw: Flexibility of intrahemispheric connections, DEN: Density, NP: Network power, GE: Global efficiency, assor: Assortativity, chapath: Characteristic path length, modu: Modularity, richclub: Rich club coefficient, trans: Transitivity, ED: Education, EDSS: Expanded disability status scale, DD: Disease duration, WMI: Working memory index, PSI: Processing speed index, FAS: Verbal fluency test, WCSTCC: Wisconsin card sorting test number of categories completes, TMTA: Trail making test a, TMTB: Trail making test B, MDITOTT: Multiscore depression inventory Total T score, STAIS: Anxiety inventory‐state, STAIT: Anxiety inventory‐transit, FSS: Fatigue severity scale) [Color figure can be viewed at http://wileyonlinelibrary.com]
