Figure 1.
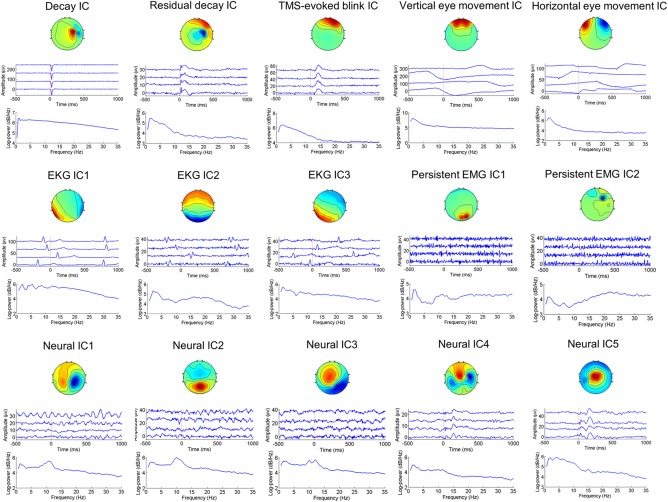
Spatio‐temporal‐spectral patterns of neural and artefactual ICA components. For each IC, the three panels are (from top to bottom) the scalp map, time courses of four exemplary epochs, and mean power spectrum across all epochs. The signs of the scalp maps and time courses are arbitrary due to the scaling ambiguity of ICA. The decay artifact includes the TMS‐evoked muscle artifact, electrode movement artifact, and electrode polarization artifact. The TMS‐evoked blink artifact is time‐locked to the TMS pulse, whereas the vertical eye movement artifact is non‐time‐locked to the TMS pulse. The EKG artifact is highly variable across subjects in its spatial distribution—the activation patterns may be rotational with respect to one another. Unlike the TMS‐evoked muscle artifact, the persistent EMG artifact is higher in frequencies and may appear in any electrodes. Neural ICs typically have dipole‐like scalp maps, and 1/f shape power spectra [Color figure can be viewed at http://wileyonlinelibrary.com]
