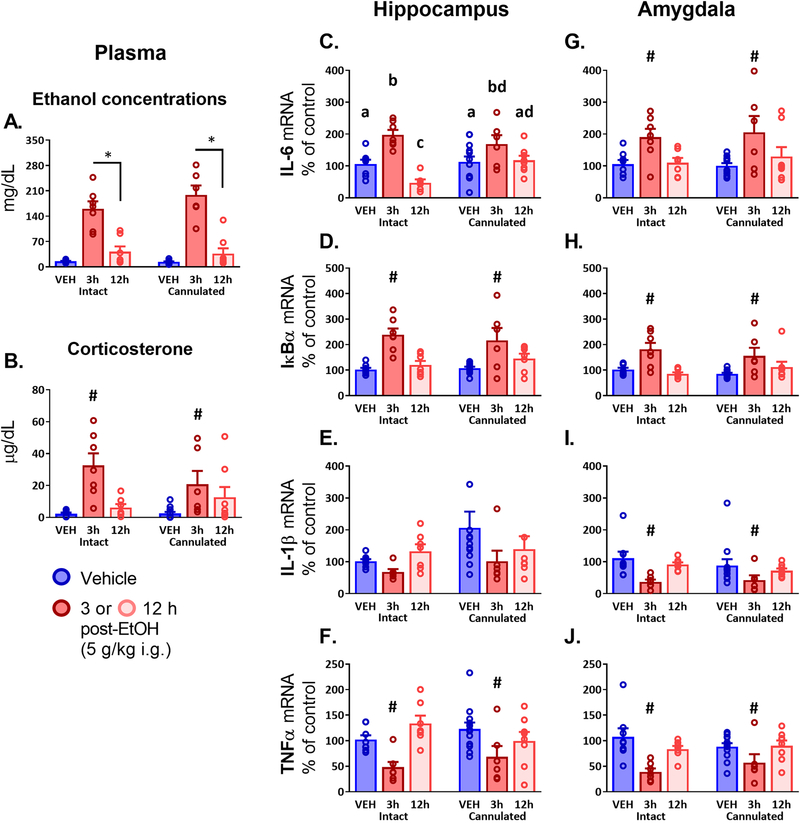
Figure 4.
Experiment 3 plasma measures and brain gene expression in adult males 3 or 12 hours after an intragastric (i.g.) intubation of vehicle (VEH) or 5 g/kg ethanol (EtOH), assayed in groups that have either been given a unilateral hippocampal cannulation (Cannulated) or remained surgically unmanipulated (Intact). Plasma measures shown include (A) ethanol concentrations and (B) corticosterone. Gene expression outcomes in the hippocampus and amygdala are shown for (C, G) Interleukin-6 - IL-6 gene expression; (D, H) Nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells inhibitor, alpha - IκBα; (E, I) Interleukin-1β - IL-1β; and (F, J) Tumor necrosis factor alpha - TNFα. In panel (A) displaying ethanol concentrations, an asterisk (*) is used to indicate a significant difference between the ethanol-intubated animals only, excluding the VEH group. Group-specific differences emerging in post hoc testing for a significant effect of Drug are indicated with a pound sign (#), indicating that the 3 h EtOH group differed significantly from both VEH and the 12 h group. Letters indicate differences divulged by post hoc testing of a significant interaction (groups that share a letter in common did not differ statistically, whereas differences between groups are indicated by letters that do not match).