Figure 2.
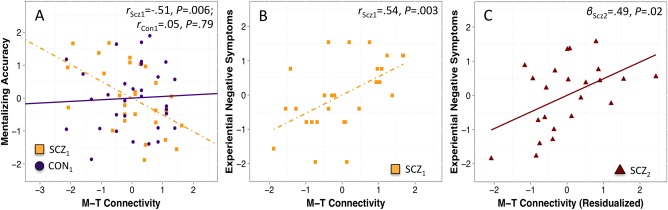
A: Group by M‐T inter‐component connectivity interaction when predicting cognitive empathy in Study 1 (i.e., SCZ Sample 1 and CON Sample 1); data illustrates the pairwise correlations for schizophrenia and control groups, separately. B: M‐T inter‐component connectivity predicts experiential negative symptoms for the schizophrenia group in Study 1. C: M‐T inter‐component connectivity predicts experiential negative symptoms for the independent schizophrenia sample in Study 2 (i.e., SCZ Sample 2); data has been residualized according to the covariates in Table III. Abbreviations: CON, control subjects; SCZ, schizophrenia subjects; M, medial prefrontal cortex and anterior cingulate cortex component; T, superior temporal gyrus, temporo‐parietal junction, and temporal poles component. [Color figure can be viewed at http://wileyonlinelibrary.com]
