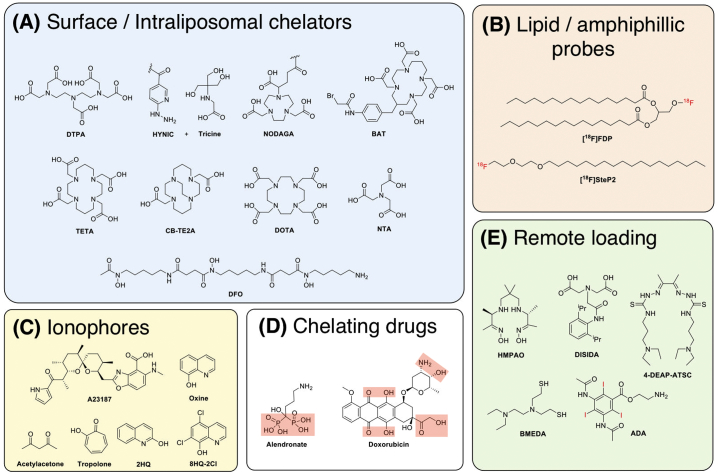
Fig. 5.
Schematic showing the chemical structures of various compounds used to assist the radiolabelling of liposomes, all of which are discussed in this review. (A) Structures of metal chelators that are either attached to the lipid surface or encapsulated inside the liposomal core, or (B) radiolabelled amphiphilic probes can be inserted into the lipid bilayer for radiolabelling. (C) Alternatively, ionophores can used to transport radionuclides inside the liposomal core and release the isotopes where they can either be trapped by binding to entrapped chelators or in some cases can bind directly to (D) the chelating groups of encapsulated drugs. (E) Radiolabelling can be also achieved by the remote loading of metal complexes or radio-iodinated compounds that become trapped in the liposomal core via protonation of the ligand used.