Figure 1.
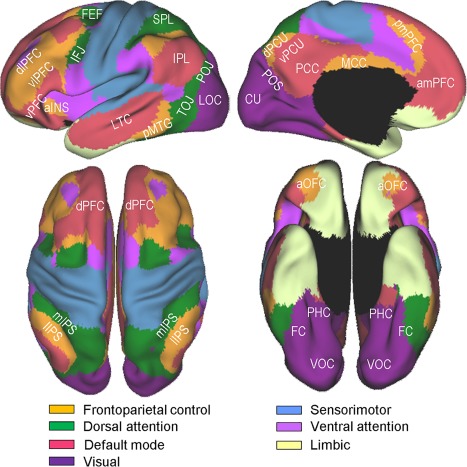
Yeo et al. [2011]'s 7‐network parcellation of the human cerebral cortex. The figures were adapted from Yeo et al. [2011] (Fig. 11) with permission from the American Physiological Society. Labeled are subregions within 4 networks, namely, the frontoparietal control, dorsal attention, visual, and default mode, which are more directly relevant to the present study. aINS, anterior insula; amPFC, anteromedial prefrontal cortex; aOFC, anterior orbitofrontal cortex; CU, cuneus; dlPFC, dorsolateral prefrontal cortex; dPCU, dorsal precuneus; dPFC, dorsal prefrontal cortex; FC, fusiform cortex; FEF, frontal eye fields; IFJ, inferior frontal junction; IPL, inferior parietal lobe; lIPS, lateral intraparietal sulcus; LOC, lateral occipital cortex; LTC, lateral temporal cortex; MCC, middle cingulate cortex; mIPS, medial intraparietal sulcus; PCC, posterior cingulate cortex; PHC, parahippocampal cortex; pmPFC, posteromedial prefrontal cortex; pMTG, posterior middle temporal gyrus; POJ parieto‐occipital junction; POS, parieto‐occipital sulcus; SPL, superior parietal lobe; TOJ, temporo‐occipital junction; vlPFC, ventrolateral prefrontal cortex; VOC, ventral occipital cortex; vPCU, ventral precuneus; vPFC, ventral prefrontal cortex. [Color figure can be viewed at http://wileyonlinelibrary.com]
