Figure 4.
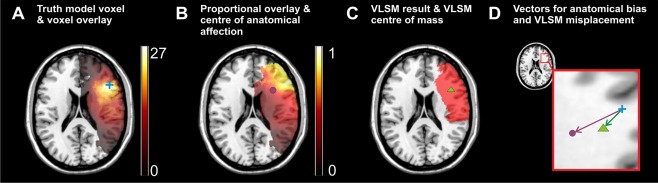
Example for the computation of voxel‐wise anatomical bias and VLBM misplacement. For one exemplary truth model voxel (MNI coordinates x = 47, y = 24, z = 20), the procedures in Experiment 2 are illustrated. (A) All lesions that include the chosen truth model voxel (blue cross) are identified to create a “voxel overlay.” (B) For each voxel damaged in at least four patients, the “voxel overlay” is element‐wisely divided by the total overlay of all 274 patients (see Fig. 1A) to produce a topography of inter‐voxel relation. The center of mass of the resulting topography (purple circle) offers a voxel‐wise center of anatomical affection. (C) The truth model voxel is used to simulate a binary “behavioral” deficit. A lesion analysis computes a statistical map (red area) and the center of mass of this map (green triangle) provides the center of VLBM results. (D) The previously defined coordinates and the truth model voxel (blue) are used to define a vector of “anatomical bias” (purple arrow) and a vector of misplacement (green arrow). All illustrations are shown on slice z = 20. Note that for the present figure the resulting centers are projected back to same z‐slice for illustration purposes. [Color figure can be viewed at http://wileyonlinelibrary.com]
