Figure 3.
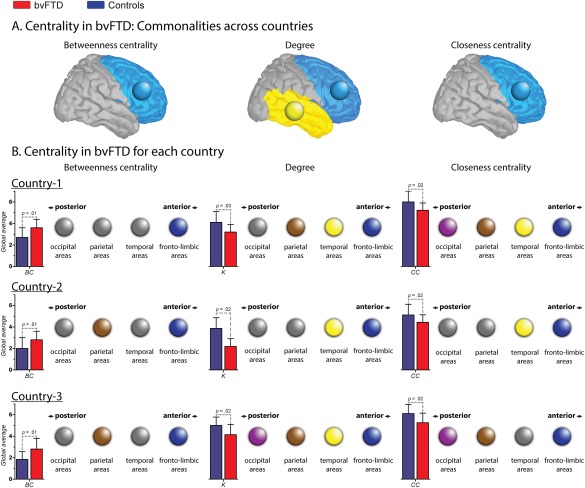
Nodal centrality features. A. Centrality in bvFTD: Communalities across countries. Circles indicate brain lobes in which the bvFTD patients presented altered areas within the same lobe across countries. In BC and CC, the common areas affected belong to the fronto‐limbic lobe, while in K, they belong both to the fronto‐limbic and temporal lobes. B. Centrality in bvFTD for each country. Color circles indicate the presence of at least one altered region within the specific lobe (pink = occipital; brown = parietal; yellow = temporal and blue = fronto‐limbic). Gray circles represent the absence of alterations within the lobe. Bar charts represent the global average (GA) of each centrality measure. Country one. Effect size of the GA of BC: 1.00. Regions with increased BC in patients: right putamen and right middle orbitofrontal cortex (fronto‐limbic areas). Effect size of the GA K: 0.91. Regions with decreased K in patients: right precentral gyrus, left rolandic operculum, right and left fusiform gyrus, right postcentral gyrus and left superior parietal cortex. Effect size of the GA CC: 0.84. Regions with decreased CC in patients: right precentral gyrus, left rolandic operculum, right and left fusiform, right postcentral gyrus, and right and left occipital inferior lobe. Country two. Effect size of the GA of BC: 0.77. Regions with increased BC in patients: left precentral gyrus, right insular cortex, right posterior cingulate cortex, right supramarginal gyrus and left angular gyrus. Effect size of the GA K: 0.75. Regions with decreased K in patients: right and left amygdala, right and left heschl's gyrus, right superior temporal pole and right middle temporal pole. Effect size of the GA CC: 0.75. Regions with decreased CC in patients: right superior frontal gyrus, left middle cingulate cortex, right and left Heschl's gyrus, right superior temporal pole, right and left middle temporal pole and right inferior temporal gyrus. Country three. Effect size of the GA of BC: 1.05. Regions with increased BC in patients: left Rolandic operculum, left medial orbitofrontal cortex, right angular gyrus and left precuneus. Effect size of the GA K: 1.00. Regions with decreased K in patients: right and left superior orbitofrontal cortex, right middle temporal pole, right paracentral lobe, right calcarine sulcus, right cuneus and lingual gyrus. Effect size of the GA CC: 0.92. Regions with decreased CC in patients: right and left superior orbitofrontal cortex, right paracentral lobe, right calcarine sulcus, and right cuneus gyrus. [Color figure can be viewed at http://wileyonlinelibrary.com]
