Figure 2.
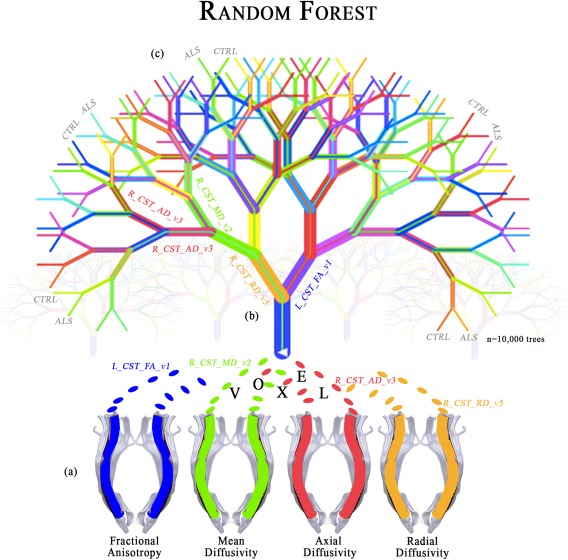
Illustration of the multivariate analysis applied in this study. (a) The dataset composed by all the corticospinal (CST) DTI voxel values of each subject, labeled by diagnosis, is used for training a forest of binary decision trees. Each voxel is labeled by side [left (L) or right (R)], followed by the related diffusion metric (FA, MD, AD, and RD) and its number (from 1 to 100). (b) Each tree is trained on a random subsample of the dataset (bootstrap). At each node a random voxel is chosen as a “splitter variable,” which attempts to separate ALS patients from healthy controls (CTRL). The more often a voxel is chosen as a splitter variable, the higher its “variable importance,” that is, the lower its Gini index. (c) Each tree of the forest gets a vote to predict new subjects. In particular, each new subject traverses each tree until it reaches a terminal node, where the class is predicted as ALS or CTRL.
