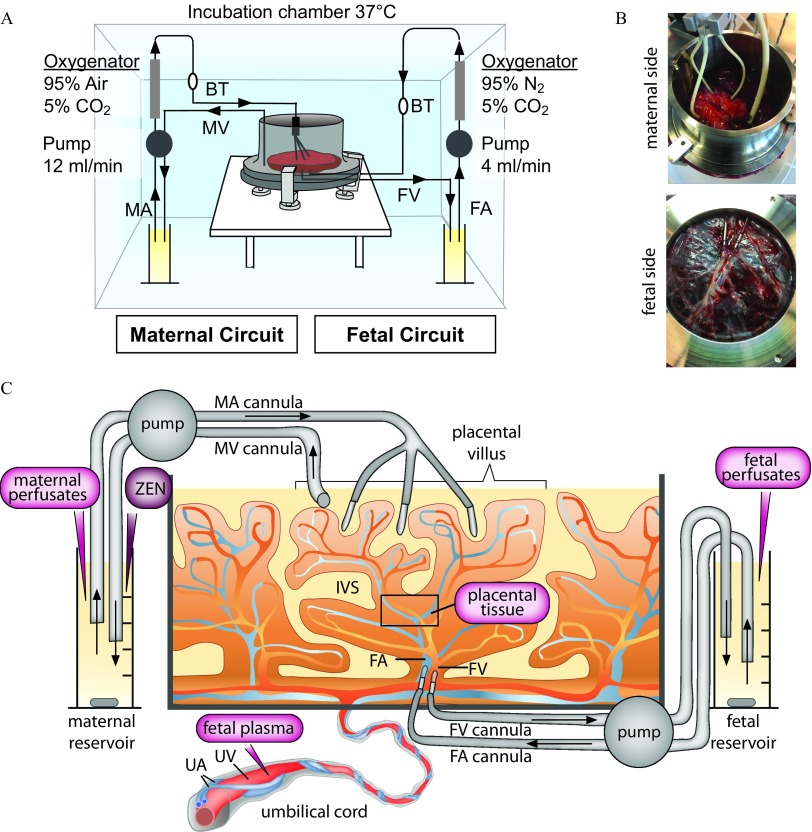
Figure 1.
Ex vivo dually perfused human placenta perfusion model. (A) Scheme of the perfusion system. (B) Photograph showing cannulation from the maternal and fetal side, respectively. (C) Scheme with details of maternal and fetal side cannulation of an intact cotyledon and sampling sites (magenta). Fetal plasma is isolated from the umbilical vein blood before perfusion. ZEN is introduced to the maternal reservoir at the start of perfusion. Maternal and fetal perfusates are sampled from the corresponding reservoirs at different time points during perfusion. Placental tissue (black quadrant) is taken from the intervillous region of a perfused cotyledon at the end of perfusion. Note: BT, bubble trap; FA, fetal artery; FV, fetal vein; IVS, intervillous space (maternal blood space); MA, maternal artery; MV, maternal vein; UA, umbilical artery; UV, umbilical vein.