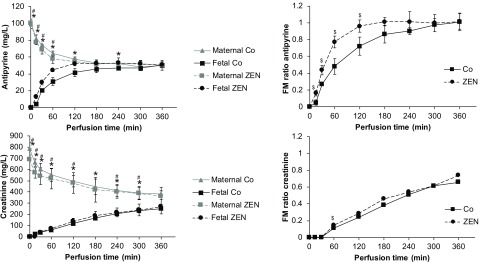
Figure 5.
Perfusion profiles and fetal–maternal (FM) ratio of the reference compounds antipyrine and creatinine. Antipyrine () and creatinine () were added to the maternal circulation in six independently perfused placentas from six different mothers (three placentas were perfused with medium without zearalenone to obtain baseline data (Co) and three placentas were perfused with medium containing ZEN). The concentrations of both reference compounds were measured from the maternal and fetal perfusates by UHPLC-MS/MS at several time points during 6 h of perfusion. Data represent of three independently perfused placentas [three control perfusions without ZEN (Co) and three perfusions with addition of ZEN (ZEN)]. is considered statistically significant (* and # denote differences between maternal and fetal concentrations in Co and ZEN perfusions, respectively; $ denotes differences in FM ratio between Co and ZEN). Perfusion data comparing maternal and fetal concentrations were analyzed by unpaired Student's t-test.