Figure 3.
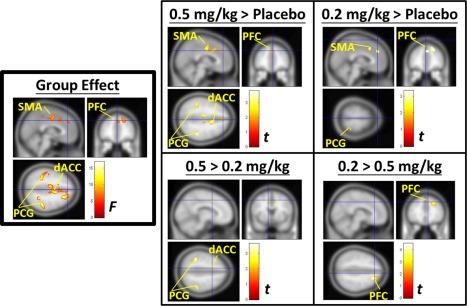
Voxel‐wise analysis showing a significant main effect of ketamine among the different groups and the post hoc analysis. Left panel: The significant main effect of the group was on the PFC, the supplementary motor area (SMA), the dorsal anterior cingulate cortex (dACC), and the bilateral post‐central gyrus (PCG). Right panel: The post hoc analyses showed that both of the ketamine groups had significantly greater increases in the SUV in the PFC, SMA, and parts of the PCG than the placebo group. The 0.5 mg/kg group (Group A) had a significantly greater increase in the SUV in the dACC and bilateral PCG than the 0.2 mg/kg group (Group B), but had a significantly lower increase in the SUV of the right‐side of the PFC than the 0.2 mg/kg group. The significance thresholds for voxel‐wise analysis were set at a voxel‐level family‐wise error (FWE)‐corrected level of P < 0.05 by two‐way group‐by‐time ANOVA. No significant main effect of time and no significant interaction between group and time were found. [Color figure can be viewed in the online issue, which is available at http://wileyonlinelibrary.com.]
