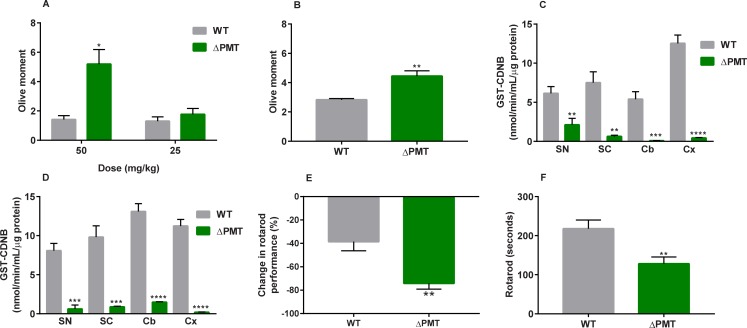
Fig 2. ΔPMT mice are susceptible to the genotoxic and neurotoxic effects of acrylamide and glycidamide.
(A, B) DNA damage in liver measured by Comet assay 24 hours after a single injection of (A) 50 or 25 mg/kg acrylamide or (B) 50 mg/kg glycidamide to male mice. DNA damage is measured as Olive Moment. Each mouse was analyzed in duplicate slides, where each slide contained >50 comets. (C, D) GST enzyme activity in nervous tissue of wild-type and ΔPMT female (C) and male (D) mice. (E) Percent change in rotarod performance relative to baseline in male mice after treatment with 200 ppm acrylamide in drinking water for 21 days. (F) Decreased rotarod performance of ΔPMT male mice compared to wild-type after treatment with 50 ppm acrylamide in drinking water for 5.5 weeks. ACR = acrylamide, SN = sciatic nerve, SC = spinal cord, Cb = cerebellum, Cx = cortex. Data analyzed by unpaired t-test between genotypes. Data represent means ± SEM, n = 4–6 (A, B), n = 5 (C, D), n = 10 (E), and n = 6–9 (F); * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001; **** p < 0.0001.