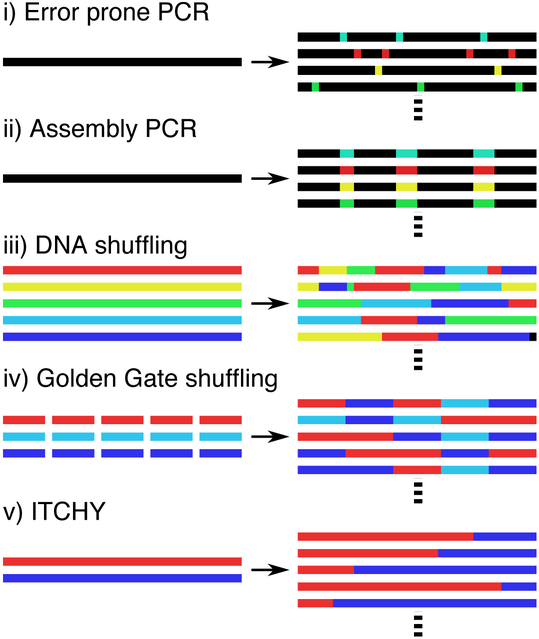
Figure 3.
Schematics of common in vitro DNA mutagenesis techniques. (i) Error prone PCR introduces mutations from a single template, producing a library of mutants. (ii) For assembly PCR, DNA oligos with random segments can be inserted into specific locations to generate diversity. (iii) DNA shuffling begins with homologous sequences for a particular function, which are digested by endonuclease and reassembled into chimeras. (iv) Golden gate shuffling can create chimeras by randomly assembling defined modular components. (v) Incremental truncation for the creation of hybrid enzymes (ITCHY) uses exonucleases to degrade the DNA and concatenate the resulting fragments.