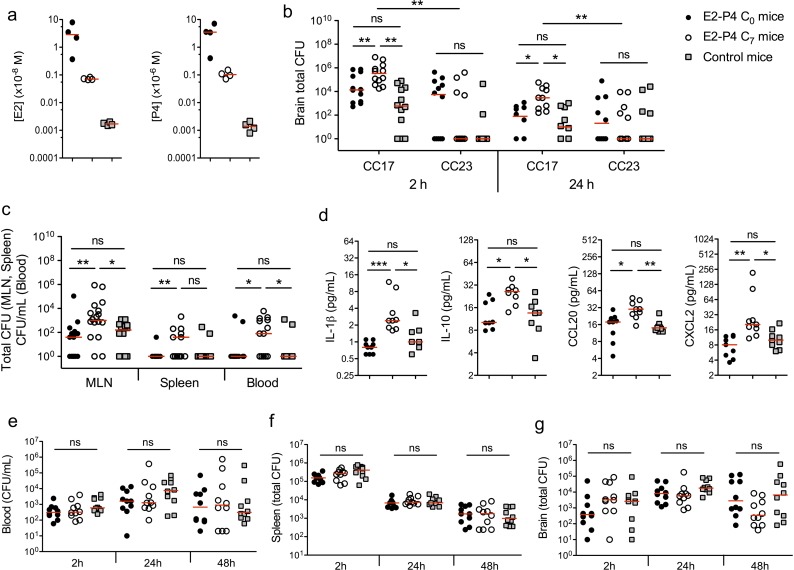
Figure 1. E2-P4 hormone levels modulate CC17 GBS dissemination and the severity of meningitis following oral infection in mice.
SPF 3-week-old mice were administered E2-P4 cocktails subcutaneously for four consecutive days leading to E2-P4 circulating levels equivalent to those found in neonates at birth (E2-P4 C0 mice) or 7 days later (E2-P4 C7 mice). Control mice were administered vehicle alone. (a) Serum levels of E2 and P4 in the 3 groups of mice measured 4 hr after the last hormonal administration (n = 4 mice per group). (b to d) Mice were gavaged with representative CC17 (strain BM110) or CC23 (strain NEM316) GBS isolates (2.1010 CFU). (b) Total CFU counts in the brain 2 hr (n = 12 mice per group) and 24 hr (n = 10 mice per group) after infection by CC17 and CC23 GBS. (c) Total CFU counts in the mesenteric lymph nodes (MLN, n = 16 mice per group), spleen (n = 12 mice per group), and blood circulating bacteria in CFU/mL (n = 12 mice per group) 2 hr after infection by CC17 GBS. (b, c) 100 represents the detection threshold. (d) Serum levels of the cytokines IL-1β, IL-10, CCL20 and CXCL2 2 hr after infection by CC17 GBS (n = 9 mice per group). (e to g) Mice were infected intravenously with CC17 GBS (2.107 CFU, n = 10 mice per group). Bacteremia (e) and total CFU counts in the spleen (f) and brain (g), 2 hr, 24 hr and 48 hr after infection. Red lines are represented at median value. Multiple-group comparisons were performed by non-parametric two-way ANOVA (b) and Kruskal-Wallis test (c to g). *p<0.05; **p<0.01; ***p<0.001; ns: not significant.