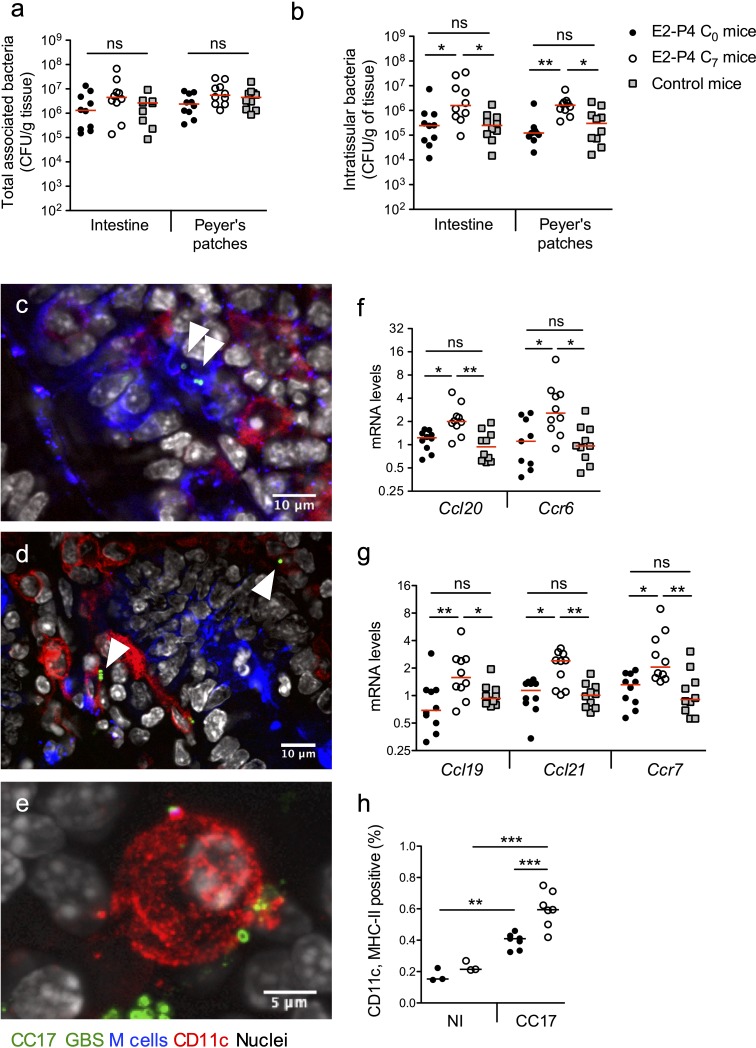
Figure 2. E2-P4 C7 concentrations favor CC17 GBS crossing of the intestinal barrier through Peyer’s patches.
SPF 3-week-old mice were administered E2-P4 cocktails for hormonal impregnation as described in Figure 1. (a, b, and f to h) Mice were gavaged by 2.1010 CFU of CC17 GBS. (a, b) Bacteria were enumerated 2 hr after infection in the intestine and Peyer’s patches either as tissue-associated bacteria (a) or as intratissular bacteria following tissue treatment with gentamicin (b). Bacterial counts are expressed in CFU per gram of tissue and were obtained following tissue homogenization and plating on Granada medium (n = 10 mice per group). (c to e) Representative confocal images (out of 12) of E2-P4 C7 mice small intestine ligated loops infected by 2.1010 CFU of CC17 GBS for 1 hr and showing intratissular bacteria (n = 3 mice). Small intestine sections showing bacteria associated with M cells (c) and CD11c positive cells (d). (e) View of a tridimensional representation of CC17 GBS associated with a CD11c positive cell. M cells were labeled with anti-UEA-I antibody, dendritic cells (DC) and macrophages with anti-CD11c antibody and nuclei with DAPI. White triangles indicate GBS cocci. (f, g) Intestinal mRNA levels of genes involved in leukocytes recruitment (f) and DC activation and migration (g) 2 hr after mouse oral gavage. Results are normalized to Actin and expressed as mean fold change relative to control condition ± SEM (n = 10 mice per group). (h) Flow cytometry analysis of CD11c and MHC-II positive cells in MLN of non-infected (NI, n = 3 mice per group) and CC17-infected mice (n = 7 mice per group) 2 hr after oral gavage of E2-P4 C0 and E2-P4 C7 mice. (a, b, and f to h) Lines are represented at median value. Multiple-group comparisons were performed by non-parametric two-way ANOVA (a, b) and Kruskal-Wallis test (f to h). *p<0.05; **p<0.01, ***p<0.001; ns: not significant.