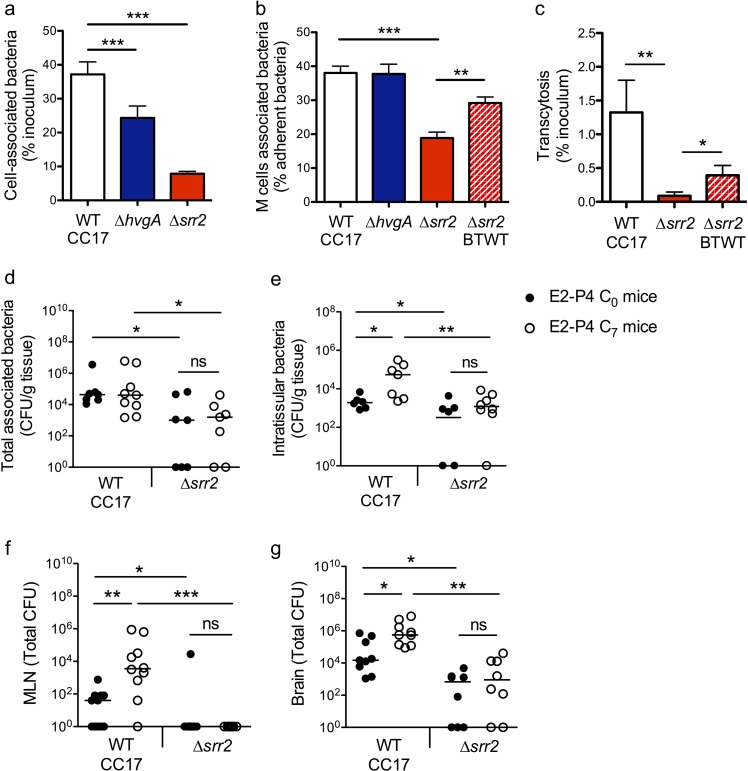
Figure 5. The CC17 surface protein Srr2 promotes GBS interaction with M cells and contributes to CC17 GBS hypervirulence in E2-P4 C7 condition.
(a to c) The epithelial monolayer composed of enterocytes and M cells was prepared as described in Figure 3 and cultured in E2-P4 C7 condition. Lymphocytes were removed before infection of the upper compartment with bacteria (multiplicity of infection 100). Cell-associated bacteria were enumerated 2 hr after infection and cells were fixed for staining. (a) Adherence of the wild-type (WT) CC17 GBS and its ∆hvgA and ∆srr2 mutants. (b) Quantitative imaging analysis of bacterial association with M cells of the WT CC17 GBS, the ∆hvgA and ∆srr2 mutants, and the ∆srr2 back to WT (BTWT) reverted mutant. (c) Transcytosis of the WT CC17 GBS, the ∆srr2 mutant, and the BTWT across the enterocytes + M cells monolayer. Results are expressed as mean ± SEM.≥3 experiments in triplicate. (d to g) SPF 3-week-old mice were administered E2-P4 cocktails as described in Figure 1 before being gavaged with the WT CC17 GBS or its ∆srr2 mutant (2.1010 CFU). Bacteria were enumerated 2 hr after infection in the Peyer’s patches either as tissue-associated bacteria (d) or as intratissular bacteria following tissue treatment with gentamicin (e), in the MLN (f), and in the brain (g). (d to f) n = 10 mice per group. (g) n = 7–9 mice per group. (d and e) Results are expressed as total CFU per gram of tissue. (f and g) Results are expressed as total CFU per organ. Lines are represented at median values. *p<0.05; **p<0.01; ***p<0.001; ns: not significant (Kruskal-Wallis test).