Figure 2.
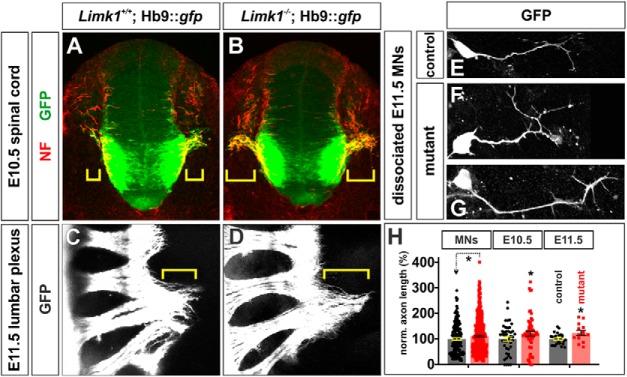
Limk1 mutant motor axons extend consistently further than control axons. A, B, In transverse sections of E10.5 spinal cord, motor axons have started to exit the lumbar spinal cord through the ventral root. Motor axon growth (brackets) is more advanced in Limk1 mutants compared with littermate controls. Motor axons were labeled by the presence of an Hb9::gfp transgene (green), and axons were labeled with antibodies against NF (red). C, D, By E11.5, motor axons have started to project beyond the lumbar plexus. Whole-mount preparations of the lumbar spinal cord show that axon growth continues to be more advanced in Limk1 mutants compared with controls. E–G, MNs were dissociated from limb-level E11.5 Limk1+/+;Hb9::gfp and Limk1−/−;Hb9::gfp spinal cords. After 20 h in culture, the Limk1 mutant GFP+ neurons had extended longer processes than the control GFP+ neurons. H, Quantification of axon lengths demonstrated that the loss of Limk1 activity results in axons that are consistently ∼15% longer than control axons (i.e., similar to the figure previously seen for dorsal sensory interneurons) (Phan et al., 2010). Dissociated MNs: The Limk1−/− GFP+ neurons (n = 446 neurons from 5 embryos; probability different from control, p < 0.028, Student's t test) extended axons that were ∼12% longer than those from the GFP+ control neurons (n = 171 neurons from 4 embryos). E10.5 spinal cord sections: The Limk1−/− motor axons (n = 155 sections from 11 embryos; probability different from control, p < 0.03) had extended ∼18% further from the ventral root of the spinal cord compared with control motor axons (n = 90 sections from 10 embryos). E11.5 spinal cord whole mounts: The Limk1−/− motor axons (n = 13 limbs taken from 8 embryos; probability different from control, p < 0.046) had extended ∼18% further from the lumbar plexus compared with control motor axons (n = 12 limbs taken from 7 embryos). Scale bars: A, B: 100 μm; C, D, 400 μm; E–G: 25 μm. Probability of similarity, *p < 0.05, Student's t-test.