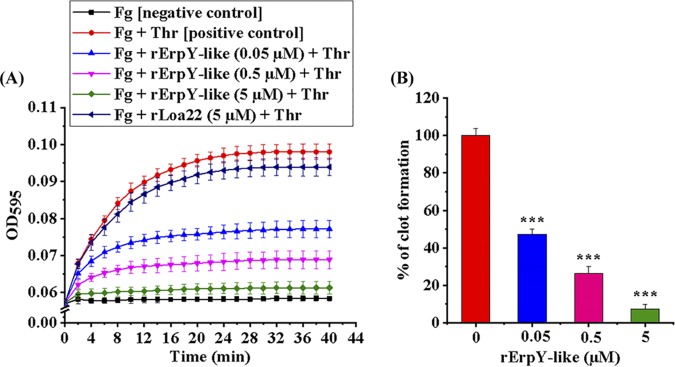
FIG 7.
Inhibition of thrombin-catalyzed fibrin clot formation in the presence of rErpY-like protein. (A) Recombinant ErpY-like protein dose-dependent inhibition of fibrin clot reaction. Increasing concentrations of rErpY-like protein (0.05 to 5 μM) were preincubated with human fibrinogen (Fg; 1 mg ml−1) in a microtiter plate for 2 h at 37°C before initiating the thrombin (Thr; 10 mU/well)-catalyzed fibrin clot formation. The clotting reaction in the well containing fibrinogen plus thrombin is taken as a positive control, while the reaction mixture containing only fibrinogen is the negative control. rLoa22 was used to check the specificity of the clot inhibition assay. The absorbance obtained during the thrombin-catalyzed fibrin clot reaction was measured every 2 min for 40 min. The recorded absorbance (595 nm) versus time (min) plot shows inhibition of thrombin-catalyzed fibrin clot formation from fibrinogen in the presence of rErpY-like protein. (B) Reduction in the percentage of fibrin clot formation in the presence of rErpY-like protein. The absorbance obtained during fibrin clot formation in the positive control of the assay shown in panel A was taken as 100%. Fibrin clot formation at a saturation time point (40 min) in the presence of an increasing concentration of rErpY-like protein was calculated as a percentage. The thrombin-catalyzed fibrin clot formation was reduced to 7% in the presence of a saturated concentration of rErpY-like protein (5 μM). The measurements were performed in triplicates, and the data shown are representative of two independent experiments. Statistical analysis was performed by the two-tailed t test (***, P < 0.001).