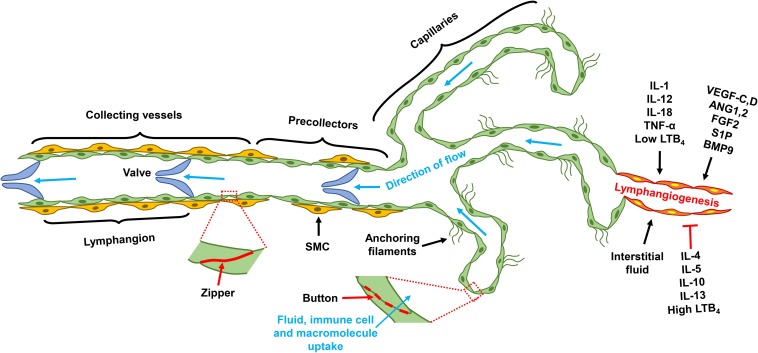
FIGURE 1.
Lymphatic vascular tree and lymphangiogenesis. Lymphatic capillaries are comprised of single layer LECs that tether directly to the extra cellular matrix. Junctional proteins form button structure that interconnects capillary LECs; and those buttons allow the formation of overlapping LEC flap, through which interstitial fluid and macromolecule enter the blind-ends of the capillaries. Capillaries converge into pre-collectors, which in turn coalesces into collecting lymphatics. SMCs loosely cover the precollector, but invest collecting lymphatics more completely. Junctional proteins of the collecting lymphatics form a continuous structure, known as zipper. Collecting lymphatics are comprised of lymphangions that are demarcated by intravascular valves, the segment between two valves is designated as one lymphangion. Factor regulates lymphangiogenesis include pro-lymphangiogenic growth factors, pro-inflammatory cytokines, and interstitial fluid. Type 2 cytokines, and high concentrations of LTB4, are molecules that suppress lymphangiogenesis. LEC, lymphatic endothelial cell; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor; ANG, angiopoietin; FGF, fibroblast growth factor; S1P, sphingosine 1 phosphate; BMP, bone morphogenetic protein; IL, interleukin; LTB4, leukotriene B4; TNF, tumor necrosis factor; SMC, smooth muscle cell.