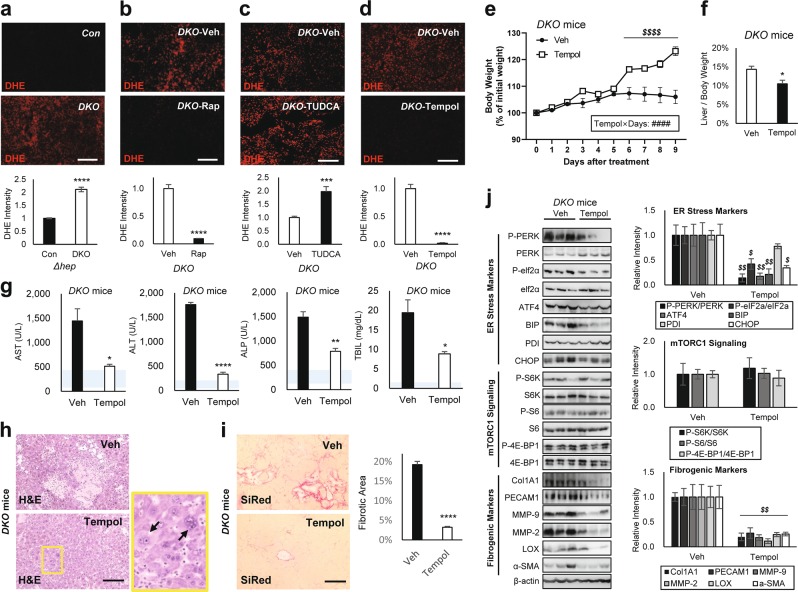
Fig. 7. Superoxide dismutase mimetic Tempol corrects DKO liver pathologies.
Mouse cohorts described in Figs. 2, 4 and 5 were analyzed. Littermate cohorts of six-week-old DKO mice were kept on vehicle drinking water (Veh) or 0.064% Tempol-containing water for 10 days (n ≥ 6). For drug treatment experiments, mice were gender-matched with both males and females. a–d Dihydroethidium (DHE) staining of liver sections and quantification. e Body weight was monitored throughout the course of the experiment. f Liver/body weight ratio was measured at the experimental endpoint. g Serum markers for liver damage were analyzed. Blue shaded regions indicate clinically normal ranges. h Liver sections were analyzed by H&E staining. Boxed area is magnified in right panel. i Liver sections were analyzed by SiRed staining. Fibrotic areas were quantified. j Liver lysates were subjected to immunoblotting (left panels) and quantification (right panels) to examine ER stress markers (top), mTORC1 signaling (middle), and fibrogenic markers (bottom). Data are presented as mean ± SEM (n = 3). *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001 (Student’s t-test). Interaction between Tempol and treatment days (Tempol × Days) were assessed through RM two-way ANOVA (####P < 0.0001), and differences in individual data points were assessed through Sidak’s multiple comparison test ($$$$P < 0.0001). For western blot quantification, the Holm–Šídák method was used to compare groups ($P < 0.05; $$P < 0.01). Scale bars, 200 µm