Figure 1.
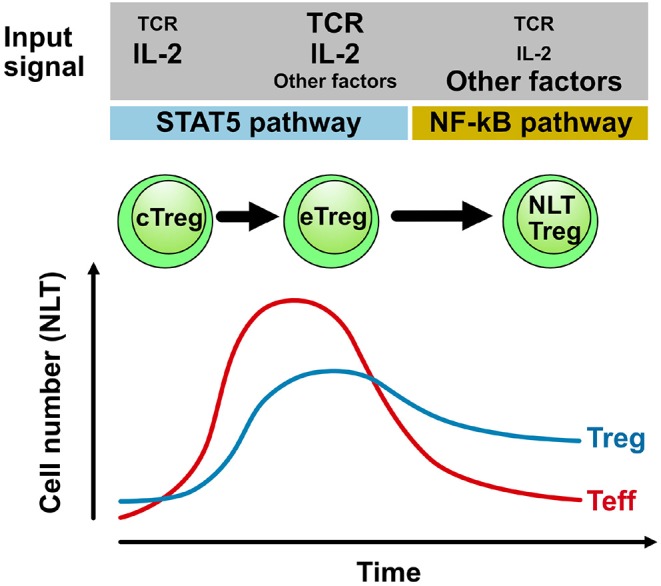
Population dynamics and maintenance of Treg cells in NLTs. During an adaptive immune response in NLT (e.g., in the central nervous system during EAE) conventional T cells (Teff) infiltrate the target tissue and expand providing sufficient IL-2 to also drive the differentiation and expansion of Treg cells. After contraction of the conventional effector T cell (Teff) population (due to active regulation by Treg cells), IL-2 becomes limiting and persisting Treg cells likely depend on alternative signals for self-renewal. Here, signals that activate the NF-κB pathway might be important cues not only for NLT function but also for their maintenance (31). TCR triggering of Treg cells and downstream modulation of the TCR signal by the transcriptional modulator IRF4 is a non-redundant event in the differentiation of central Treg cells (cTreg) in secondary lymphoid tissues into effector Treg cells (eTreg) in the inflamed tissue. The requirement of the TCR signal and other cues in NLT Treg cells that reside in specific niches over extended periods of time needs to be determined and likely depends on the anatomical niche that might then also drive a distinct functional specialization of NLT Treg cells.
