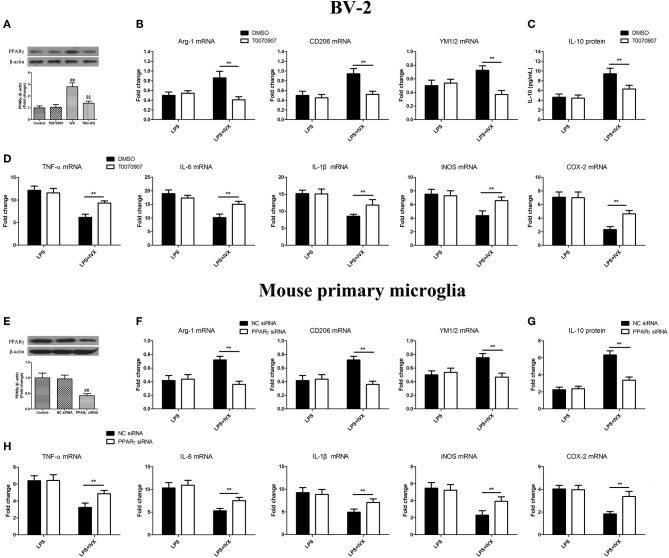
Figure 3.
PPARγ activation is involved in IVX-mediated microglial polarization in LPS- induced BV-2 cells and mouse primary microglia. (A) After treatment with T0070907 (an inhibitor of PPARγ) for 2 h and PPARγ siRNA for 24 h and then IVX for 2 h in BV-2 cells and mouse primary microglia, the protein expression of PPARγ was measured with Western blotting. Following pretreatment with 5 μM T0070907 for 2 h and PPARγ siRNA for 24 h, cells were treated with IVX (200 μg/mL) for 2 h and then stimulated with LPS (100 ng/mL) for 6 h. (E) The protein expression of PPARγ was detected via Western blotting. (B,F) The mRNA expression of M2 microglial markers (Arg-1, CD206, and YM1/2) were detected via RT-PCR. (D,H) The mRNA expression of M1 microglial markers (TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β, iNOS, and COX-2) were detected via RT-PCR. Pretreatment with 5 μM T0070907 for 2 h and PPARγ siRNA for 24 h, cells were treated with IVX (200 μg/mL) for 2 h and then stimulated with LPS (100 ng/mL) for 24 h. (C,G) The release of IL-10 was measured with ELISA. The experiments were conducted in triplicate and repeated at least three times. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM (n = 4 in each group). ##p < 0.01, vs. control group; $$p<0.01, vs. IVX group; **p< 0.01, T0070907 or PPARγ siRNA + LPS + IVX group vs. LPS + IVX group.