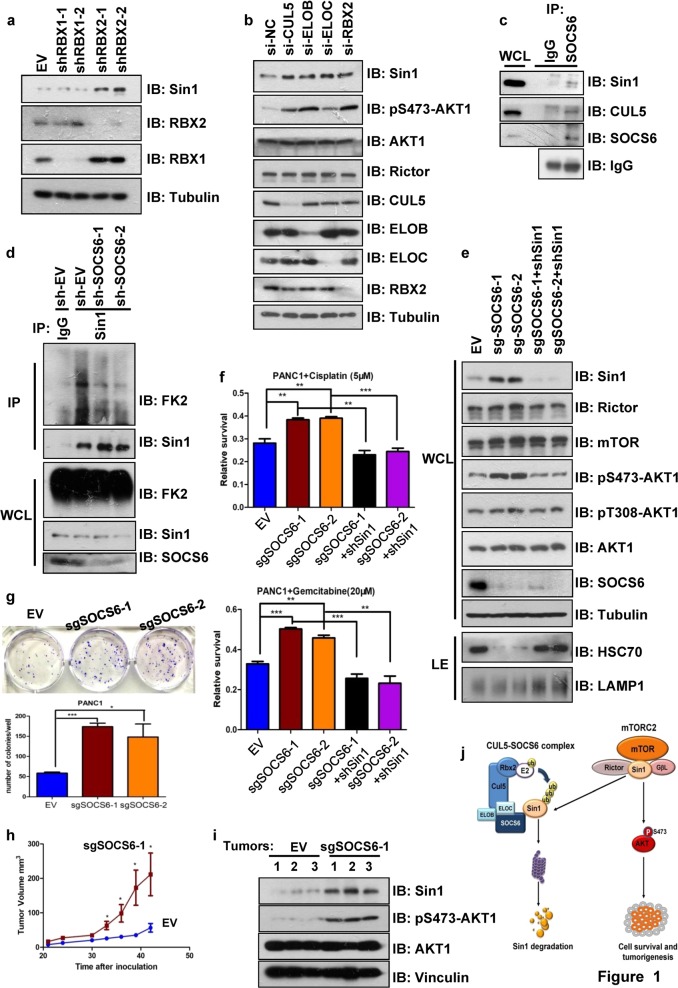
Fig. 1. The CUL5-SOCS6 E3 complex promotes Sin1 degradation, and regulates cell survival and tumorigenesis.
a, b Depletion of RBX2 (a), ElonginB/C, and CUL5 (b) upregulated Sin1 in 293T cells. c The interaction of SOCS6 and Sin1 was detected at endogenous level in 293T cells. MG132 was added 12 h prior to cell harvest for immuno-precipitation.WB was detected with indicated antibodies as shown. d Knockdown of SOCS6 decreased endogenous Sin1 ubiquitination in 293T cells. Cells were treated with shRNAs targeting SOCS6 and cell lysates were made after MG132 treatment (12 h) for immunoprecipitation and detected with indicated antibodies. FK2 detected ubiquitinated proteins. e Lentiviral sgRNAs-mediated SOCS6 knockout (ko) elevated Sin1 expression and subsequently activated mTORC2 in PANC1 cells, while Sin1 knockdown reversed such effect. f SOCS6 ko PANC1 cells from (e) were more resistant to Cisplatin or Gemcitabine treatment. Data are mean ± SEM (n = 3), **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, Student’s t-test. g SOCS6 ko PANC1 cells from (e) formed more colonies than control cells in anchorage dependent growth condition. Data are mean ± SEM (n = 3), *P < 0.05 ***P < 0.001, Student’s t-test. h, i SOCS6 ko PANC1 cells were more potent in xenograft tumorigenesis assay (h), which may be caused by elevated mTORC2-AKT1 pathway (i). For (h), data are mean ± SEM (n = 6), *P < 0.05, Student’s t-test. Lysates of 3 tumors from each group were prepared and analyzed in (i). j The schematic model of how the CUL5-SOCS6 complex regulates mTORC2 function via Sin1 degradation