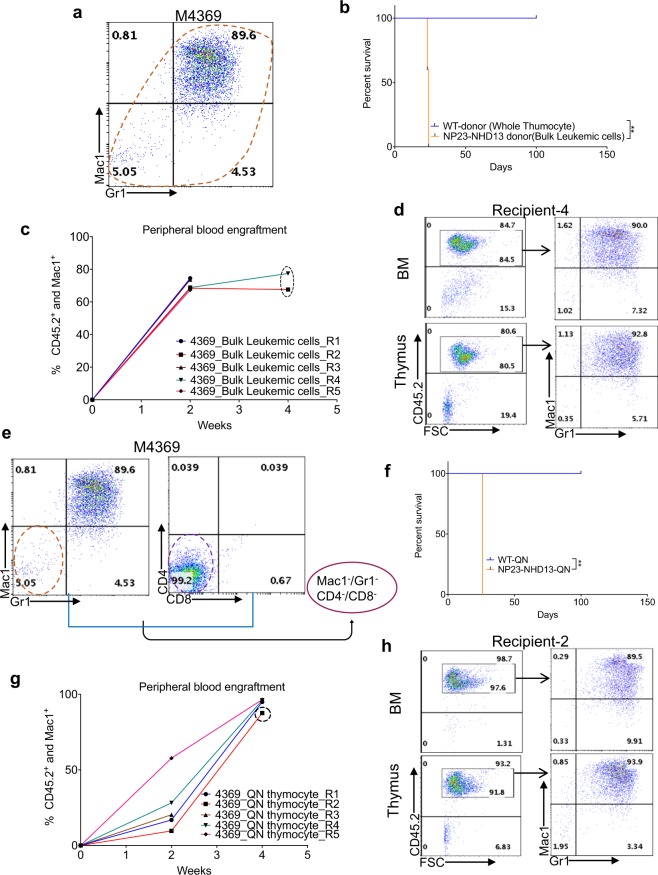
Figure 4.
Thymic AML is transplantable. (a) Flow cytometry of thymus invaded by AML cells (#4369). (b) Survival of WT (total thymocytes) and NP23-NHD13 (bulk thymic AML cells) transplant recipients, 1 × 106 cells /mouse, n = 5 mice per group. Data are analyzed by Log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test. (c) Engraftment of CD45.2+/Mac1+ cells at indicated time points (dotted circle at 4 wk time point indicates engraftment data from BM). (d) Flow cytometry of representative transplant recipient (R-4) shows engraftment of leukemic myeloid cells in both BM and thymus. (e) Quadruple negative (QN) thymocytes (Mac1−/Gr1− and CD4−/CD8−, 8.4 × 104 cells/mouse) transplanted from donor #4369, WT-QN thymocytes (9.6 × 104 cells/mouse) are used as control, n = 5 mice per group. (f) Survival of WT and NP23-NHD13 (QN) transplant recipients analyzed by Log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test. (g) Engraftment of CD45.2+/Mac1+ cells at indicated time points (dotted circle at 4 wk time point indicates engraftment data from BM). (h) Flow cytometry of representative transplant recipient (R-2) indicates engraftment and myeloid commitment of the transplanted QN thymocytes in BM and thymus. **P < 0.01.