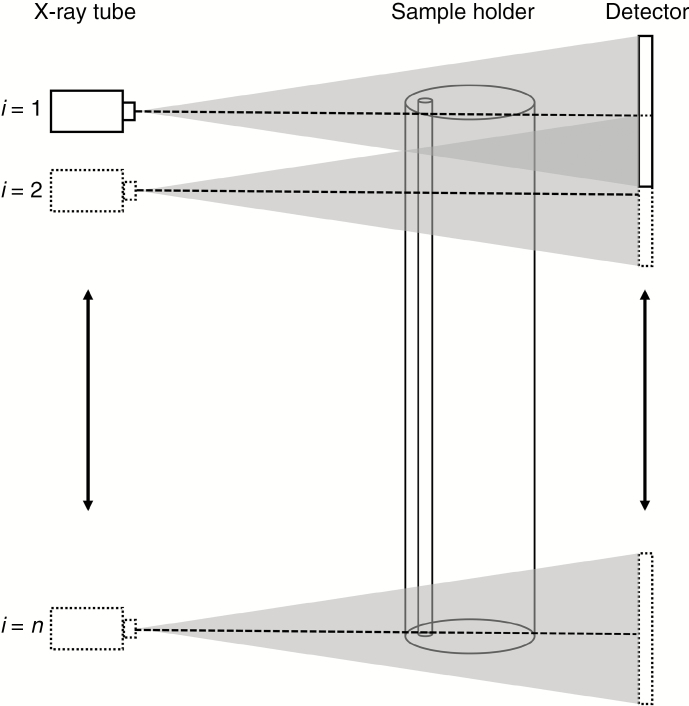
Fig. 1.
Principle of stacked scanning: tube and detector move simultaneously and, at each position, i, a full tomography scan is made of the samples in the sample holder, ensuring a pre-defined overlap with the previous scan. The total number of scans is n. Note that instead of moving the tube and detector, the sample could move upwards (or downwards) as well. The dotted line in the centre of the beam represents the central plane.