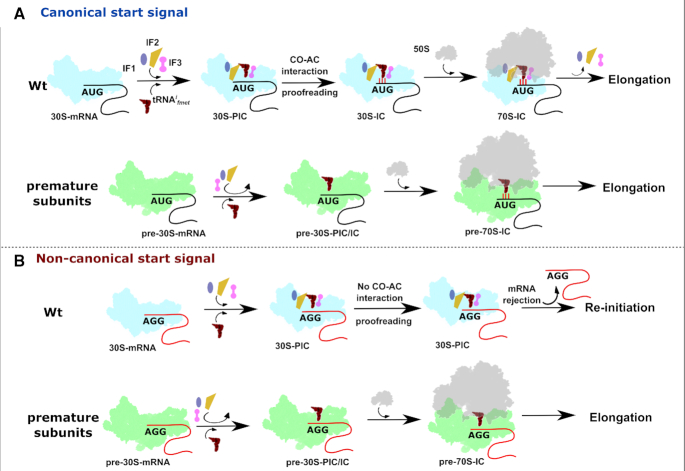
Figure 8.
A schematic representation of the plausible events leading to the participation of premature subunits in translation. (A) Initiation factors and tRNAifmet are recruited to mature 30S subunits complexed with mRNA harbouring canonical start signal to form accurate initiation intermediates. These intermediates undergo meticulous kinetic proofreading checkpoints posed by initiation factors and only then are allowed to enter the translation cycle. On the contrary, premature subunits with structural deformities possess weak binding affinities for initiation factors thus readily bind to 50S particles to initiate translation from canonical start signals. (B) Mature 30S particles can form pre-initiation complexes on non-canonical signals, but proofreading of the impaired codon–anticodon interaction by initiation factors pre-empts their transition into initiation complexes and further translation. However, due to the weak binding of Initiation factors, premature 30S particles elude such proofreading checkpoints to form 70S-IC, which initiates protein synthesis from non-canonical initiation signals thus displaying compromised fidelity of translation initiation.