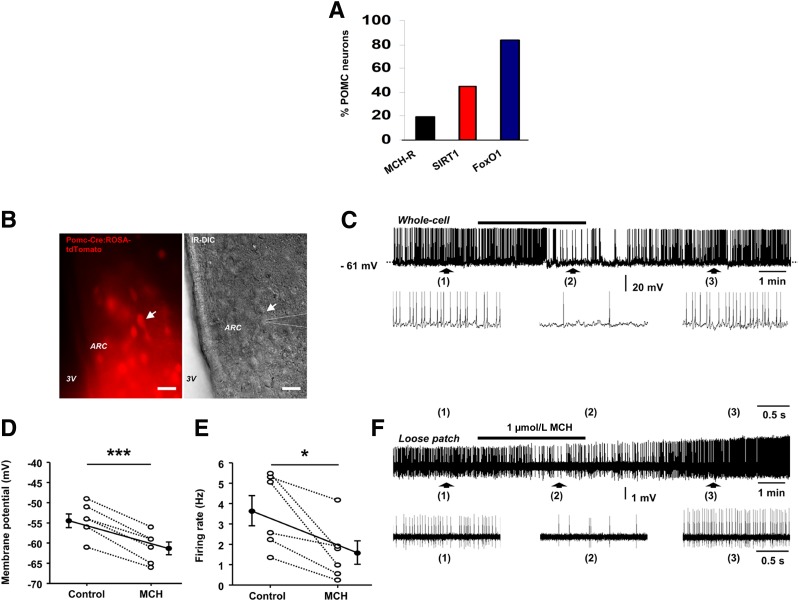
Figure 2.
MCH inhibits the activity of POMC neurons in the ARC. A: FACS sorting and single-cell RNA sequencing of POMC-EGFP neurons showing MCHR, SIRT1, and FoxO1 expression (GEO Database repository, GEO Accession: GSE92707). B: Left, a spontaneously fluorescent ARC POMC neuron (arrow) from a Pomc-Cre:ROSA-tdTomato mouse was identified for patch-clamp recording; right, infrared differential interference contrast (IR-DIC) of the same image showing a patched pipette (dotted lines) placed on the cell membrane of the identified POMC neuron (arrow). Scale bars = 50 μm. C: Whole-cell current-clamp recording showing that MCH reversibly decreased the spontaneous firing activity of the POMC neuron patched in B. Note that the inhibitory effect was accompanied by a membrane hyperpolarization. Denoted regions of the recording are shown underneath with an expanded time scale. D: Average membrane potential of ARC POMC neurons in control conditions and in the presence of MCH (n = 6 cells from four mice). ***P ≤ 0.001 by paired t test. E: Average firing rate of ARC POMC neurons in control conditions and in the presence of MCH (n = 6 cells from four mice). *P ≤ 0.05 by paired t test. F: Trace showing that MCH reduced the spontaneous firing activity of another ARC POMC neuron recorded in loose patch configuration. Pooled data are shown as mean ± SEM. *P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.01, and ***P ≤ 0.001 vs. controls.