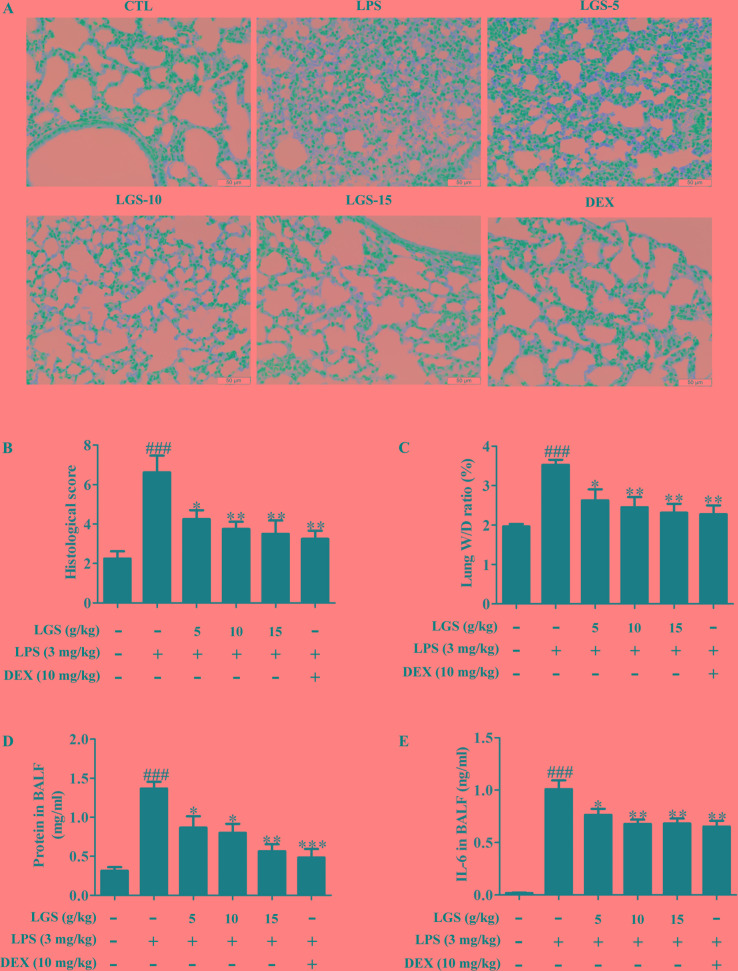
Figure 6.
LGS attenuates acute lung injury in mice. After being intragastric administered with LGS (5 g/kg, 10 g/kg, 15 g/kg) or DEX (10 mg/kg) for 7 days, respectively. LPS (3 mg/kg) was intratracheally instilled to induce the ALI model. The mice were anesthetized with 1.5% (w/v) pentobarbital sodium solution to acquire bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) samples and lung tissues. (A−B) LGS ameliorates the pathological changes in ALI mice. After H & E staining, the tissue sections were observed (A, 400 ×) and the histological score were estimated (B). (C−D) LGS decreases the capillary permeability of lung tissues in ALI mice. (C) Lung W/D ratio was detected by electronic scales (D) and the protein content in BALF was measured by BCA assay. (E) LGS decreases inflammation of lung tissues in ALI mice. The level of IL-6 in BALF was determined by ELISA. Data are represented as the mean ± SEM. ### P < 0.001 versus control, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001 versus LPS treatment by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s test.