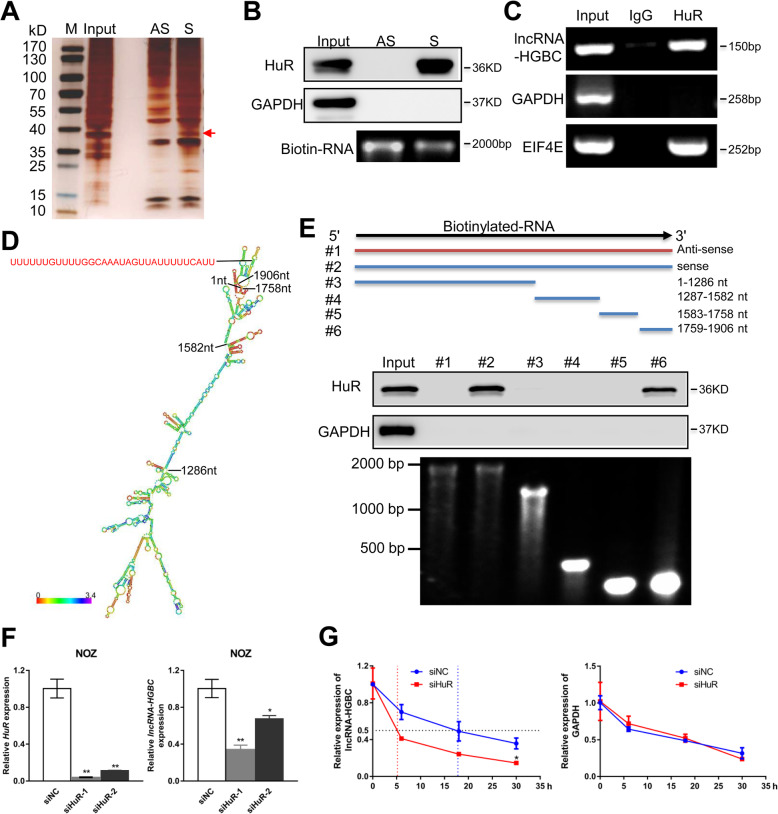
Fig. 4.
HuR physically interacts with and stabilizes lncRNA-HGBC. a RNA pull down assay by lncRNA-HGBC and its antisense RNA followed by silver staining of protein extract from NOZ cells. A band indicated by an arrow was excised for mass spectrometry analysis. S: sense strand of lncRNA-HGBC, AS: anti-sense strand of lncRNA-HGBC. b Western blot analysis of the specific association of HuR and lncRNA-HGBC. GAPDH was used as the negative control. S: sense strand of lncRNA-HGBC, AS: anti-sense strand of lncRNA-HGBC. c RIP experiments were performed using an antibody against HuR on NOZ cell extracts followed qRT-PCR. GAPDH and EIF4E were served as the negative and positive control, respectively. d The predicted secondary structure of lncRNA-HGBC. e Immunoblotting of HuR in pull-down samples by full-length biotinylated-lncRNA-HGBC (#2), antisense lncRNA-HGBC (#1) or truncated biotinylated-lncRNA-HGBC fragments (#3: 1–1286 nt; #4: 1287–1582 nt; #5: 1583–1758 nt; #6: 1759–1906 nt), with GAPDH as the negative control. The bottom image showed each transcribed RNA. f qRT-PCR analysis of HuR and lncRNA-HGBC levels in HuR-depleted NOZ cells. g NOZ cells transfected HuR siRNA or siNC were treated with α-amanitin (50 mM) to block new RNA systhesis and the levels of lncRNA-HGBC and β-actin were assessed by qRT-PCR analysis and normalized to 18S rRNA (a product of RNA polymerase I that is unaffected by α-amanitin). All values at time 0 h were normalized to 1. ***P < 0.001, **P < 0.01, *P < 0.05