Figure 1.
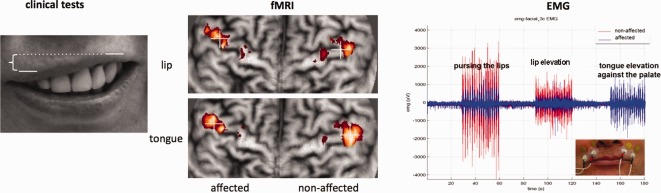
Illustration of tests and investigations performed. Left: Clinical test: Schematic image of the condition “lip elevation.” The patient shows right‐sided facial palsy. Comparison of distance difference between the superior border of the upper lip between facial sides. Middle: Demonstration of the flattening method for the same patient. The left cortical hemisphere is the affected (deafferented) side (anterior is superior). Crosses illustrate the COG of the activation cluster within the precentral gyrus. Right: EMG‐recordings of the superior orbicularis oris of the affected (blue) and the nonaffected (red) side during “pursing the lips,” “lip elevation” and “tongue elevation against the palate.” Only the affected side shows high coactivation during tongue elevation movement although it is less active during both other movements. [Color figure can be viewed in the online issue, which is available at http://wileyonlinelibrary.com.]
