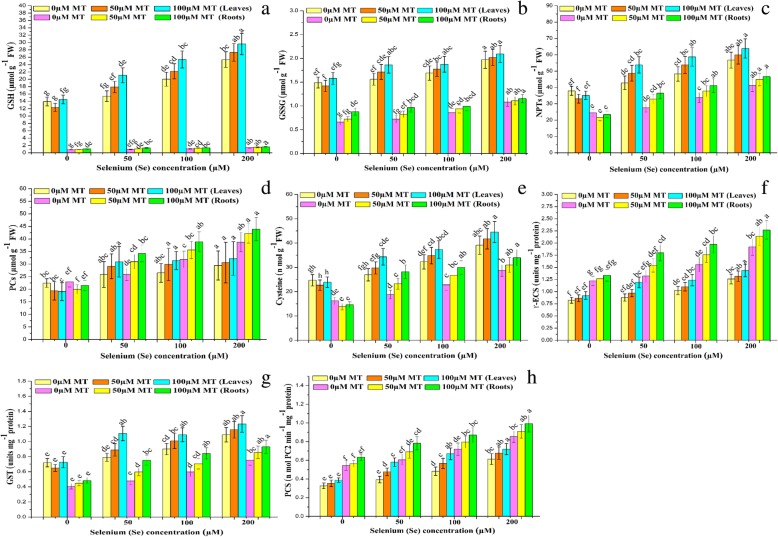
Fig. 4.
Interactive effects of exogenous melatonin and selenium on the biosynthesis of thiolic components and their metabolic enzymes. Effects of different treatments of exogenous melatonin (MT) (0 μM, 50 μM and 100 μM) and selenium (Se) (0 μM, 50 μM, 100 μM and 200 μM) on the (a) reduced glutathione content (GSH) (μmol g− 1 FW), (b) oxidized glutathione content (GSSG) (μmol g− 1 FW), (c) non-protein thiols (NPTs) (μmol g− 1 FW), (d) phytochelatins (PCs) (μmol g− 1 FW), (e) cysteine (Cyst) (nmol g− 1 FW), and (f) activities of γ-glutamylcysteine synthetase (γ-ECS) (units mg− 1 protein), (g) glutathione-S-transferase (GST) (units mg− 1 protein) and (h) phytochelatins synthase (PCS) (nmol PC2 min− 1 mg− 1 protein) in the leaves and roots of Brassica napus cv. ZS 758