Figure 3.
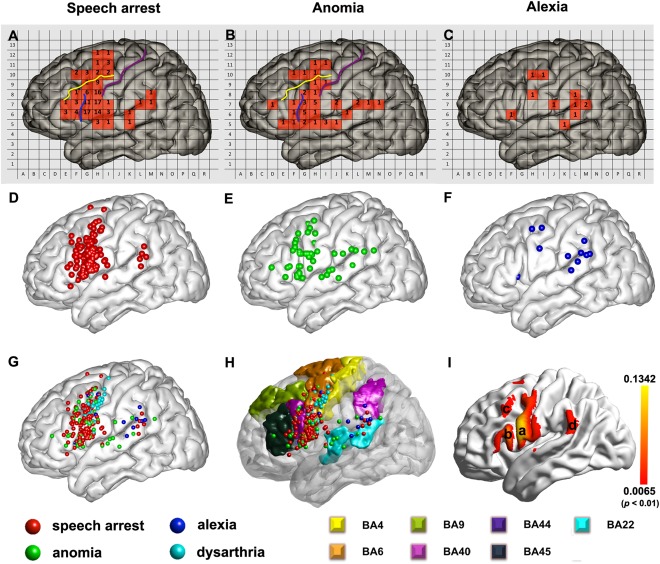
Three types of language maps for Chinese. (A, B, and C) The total number of positive sites for speech arrest, anomia and alexia in relevant landmarks in a 2D patch‐like view. (D, E, and F) 3D scatter maps of the ISM positive sites for speech arrest, anomia, and alexia. (G) The combination of all ISM positive sites, including speech arrest, anomia, alexia and dysarthria (this condition was shown to differentiate from the speech arrest condition because dysarthria was only caused by motor responses in the mouth or pharyngeal muscle). (H) The relationship between the ISM positive sites and the typical language‐related Brodmann areas (BA). (I) ALE map for speech arrest. (For detailed ALE statistics map generation method, please see Supporting Information). Region (a): ventral precentral gyrus, (b): pars opercularis, (c): middle frontal gyrus, (d): temporo‐parietal junction. The threshold was P < 0.01, uncorrected (the corresponding value of ALE statistics threshold was 0.0065).
