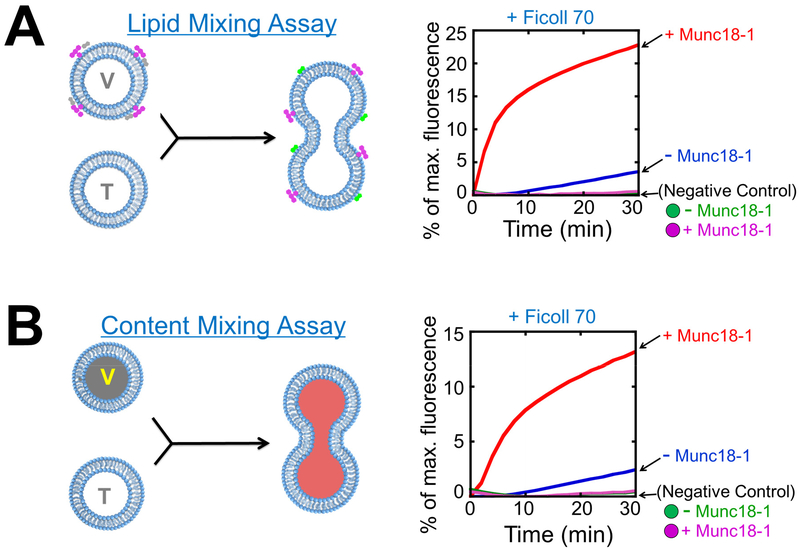
Figure 2. Reconstitution of SNAREs and SM proteins in liposome fusion assays.
A) Left: diagram showing the Förster/fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET)-based assay that measures the lipid mixing of liposome fusion reaction. When unlabeled t-SNARE liposomes fuse with NBD/rhodamine-labeled v-SNARE liposomes, NBD fluorescence increases due to diminished NBD-rhodamine FRET. For clarity, proteins and crowding agents are not shown. Right: liposome lipid mixing reactions. The t-SNARE liposomes containing syntaxin-1 and SNAP-25 were directed to fuse with VAMP2 liposomes with or without 5 μM Munc18-1. The reactions were carried out in the presence of 100 mg/mL Ficoll 70. Ingredients of the samples were mixed and immediately loaded into a pre-warmed microplate to initiate fusion. In negative controls, VAMP2 CD was added to the reactions to the final concentration of 20 μM. B) Left: diagram showing the assay that measures the content mixing of liposome fusion reaction. In these assays, unlabeled t-SNARE liposomes are mixed with sulforhodamine B-loaded v-SNARE liposomes in which the sulforhodamine B fluorescence is inhibited by self-quenching. The fusion of the liposomes leads to the mixing of their contents and the dequenching of sulforhodamine B fluorescence. Right: liposome content mixing reactions. The fusion reactions were performed as in A. Adapted with permission from reference (33). Copyright 2015 American Chemical Society.