Figure 3.
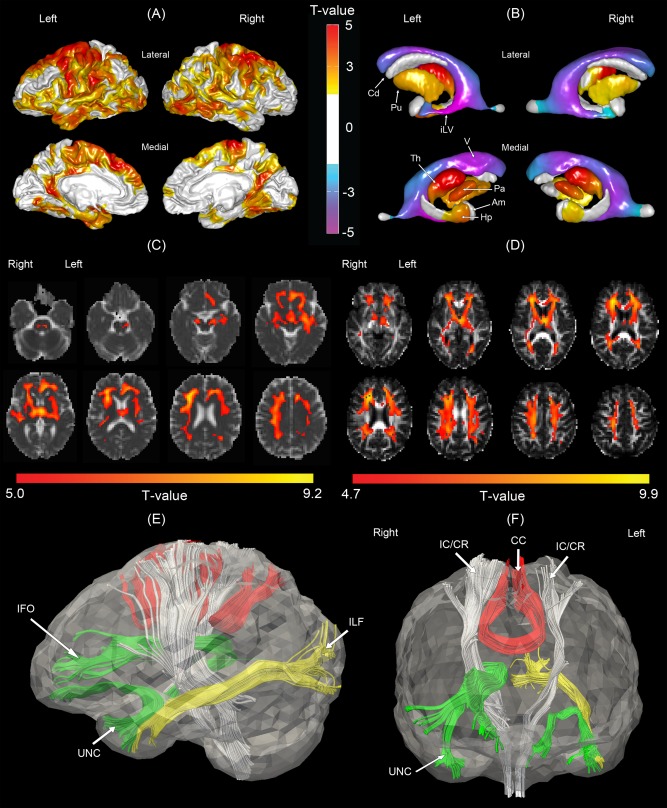
Morphological comparisons between the normal control and moderate to severe vascular cognitive impairment (MSVCI) groups. (A) Statistical map of cortical thickness. Warmer color indicates more severe cortical thinning in the MSVCI group as compared to the NC group. (B) Statistical map of subcortical shapes. Warmer color indicates more severe subcortical shrinkage and cooler colors indicates greater ventricular enlargement in the MSVCI group as compared to the NC group. (C) Statistical map of mean diffusivity (MD). Warmer color indicates more severe subcortical shrinkage and cooler color indicates greater ventricular enlargement in the MSVCI group as compared to the NC group. (D) Statistical map of generalized fractional anisotropy (GFA). Brighter color indicates smaller GFA in the MSVCI group. Panels (E, F) illustrate affected fiber bundles passing through the regions highlighted in panel (C), which were determined in the atlas using HARDI tractography technique. Am, amygdala; Cd, caudate; Hp, hippocampus; iLV, inferior lateral ventricle; Pa, globus pallidus; Th, thalamus; V, ventricle; CC, corpus callosum; IC/CR, internal capsule/corona radiata; IFO, inferior fronto‐occipital fasciculus; ILF, inferior longitudinal fasciculus; UNC, uncinate fasciculus. [Color figure can be viewed in the online issue, which is available at http://wileyonlinelibrary.com.]
